Continuous flow enantioselective arylation of aldehydes with ArZnEt using triarylboroxins as the ultimate source of aryl groups
- PMID: 20126636
- PMCID: PMC2813714
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.5.56
Continuous flow enantioselective arylation of aldehydes with ArZnEt using triarylboroxins as the ultimate source of aryl groups
Abstract
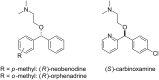
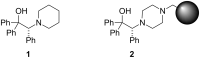
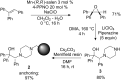
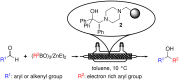
A continuous flow system for the synthesis of enantioenriched diarylmethanols from aldehydes is described. The system uses an amino alcohol-functionalized polystyrene resin as the catalyst, and the arylating agent is conveniently prepared by transmetallation of triarylboroxins with diethylzinc.
Keywords: asymmetric synthesis; continuous flow; diarylmethanols; solid-supported catalyst; triarylboroxins.
Figures
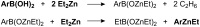
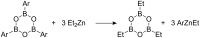


Similar articles
-
Silica-Supported Catalyst for Enantioselective Arylation of Aldehydes under Batch and Continuous-Flow Conditions.Org Lett. 2018 May 4;20(9):2737-2740. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00945. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Org Lett. 2018. PMID: 29667841
-
Diastereomeric aziridine carbinol catalyzed enantioselective arylation reaction: toward the asymmetric synthesis of both enantiomers of chiral 3-aryl phthalide.J Org Chem. 2014 Jul 3;79(13):6087-93. doi: 10.1021/jo500796w. Epub 2014 Jun 13. J Org Chem. 2014. PMID: 24912109
-
Application of beta-hydroxysulfoximines in catalytic asymmetric phenyl transfer reactions for the synthesis of diarylmethanols.J Org Chem. 2007 Nov 9;72(23):8859-62. doi: 10.1021/jo7016718. Epub 2007 Oct 11. J Org Chem. 2007. PMID: 17929870
-
Catalytic asymmetric approaches towards enantiomerically enriched diarylmethanols and diarylmethylamines.Chem Soc Rev. 2006 May;35(5):454-70. doi: 10.1039/b600091f. Epub 2006 Mar 16. Chem Soc Rev. 2006. PMID: 16636728 Review.
-
Catalytic asymmetric organozinc additions to carbonyl compounds.Chem Rev. 2001 Mar;101(3):757-824. doi: 10.1021/cr000411y. Chem Rev. 2001. PMID: 11712502 Review.
Cited by
-
Continuous-flow enantioselective α-aminoxylation of aldehydes catalyzed by a polystyrene-immobilized hydroxyproline.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011;7:1486-93. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.7.172. Epub 2011 Oct 31. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011. PMID: 22238521 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous-flow catalytic asymmetric hydrogenations: Reaction optimization using FTIR inline analysis.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2012;8:300-7. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.8.32. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2012. PMID: 22423298 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous-flow hydration-condensation reaction: Synthesis of α,β-unsaturated ketones from alkynes and aldehydes by using a heterogeneous solid acid catalyst.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011;7:1680-7. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.7.198. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2011. PMID: 22238547 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
