Functional reconstitution into liposomes of purified human RhCG ammonia channel
- PMID: 20126667
- PMCID: PMC2812482
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008921
Functional reconstitution into liposomes of purified human RhCG ammonia channel
Abstract
Background: Rh glycoproteins (RhAG, RhBG, RhCG) are members of the Amt/Mep/Rh family which facilitate movement of ammonium across plasma membranes. Changes in ammonium transport activity following expression of Rh glycoproteins have been described in different heterologous systems such as yeasts, oocytes and eukaryotic cell lines. However, in these complex systems, a potential contribution of endogenous proteins to this function cannot be excluded. To demonstrate that Rh glycoproteins by themselves transport NH(3), human RhCG was purified to homogeneity and reconstituted into liposomes, giving new insights into its channel functional properties.
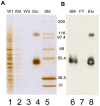
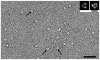
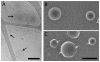
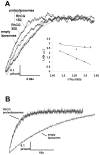
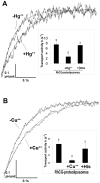
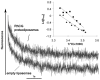
Methodology/principal findings: An HA-tag introduced in the second extracellular loop of RhCG was used to purify to homogeneity the HA-tagged RhCG glycoprotein from detergent-solubilized recombinant HEK293E cells. Electron microscopy analysis of negatively stained purified RhCG-HA revealed, after image processing, homogeneous particles of 9 nm diameter with a trimeric protein structure. Reconstitution was performed with sphingomyelin, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidic acid lipids in the presence of the C(12)E(8) detergent which was subsequently removed by Biobeads. Control of protein incorporation was carried out by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. Particle density in liposomes was a function of the Lipid/Protein ratio. When compared to empty liposomes, ammonium permeability was increased two and three fold in RhCG-proteoliposomes, depending on the Lipid/Protein ratio (1/300 and 1/150, respectively). This strong NH(3) transport was reversibly inhibited by mercuric and copper salts and exhibited a low Arrhenius activation energy.
Conclusions/significance: This study allowed the determination of ammonia permeability per RhCG monomer, showing that the apparent Punit(NH3) (around 1x10(-3) microm(3)xs(-1)) is close to the permeability measured in HEK293E cells expressing a recombinant human RhCG (1.60x10(-3) microm(3)xs(-1)), and in human red blood cells endogenously expressing RhAG (2.18x10(-3) microm(3)xs(-1)). The major finding of this study is that RhCG protein is active as an NH(3) channel and that this function does not require any protein partner.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human Rhesus B and Rhesus C glycoproteins: properties of facilitated ammonium transport in recombinant kidney cells.Biochem J. 2005 Oct 1;391(Pt 1):33-40. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050657. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15929723 Free PMC article.
-
Relative CO₂/NH₃ permeabilities of human RhAG, RhBG and RhCG.J Membr Biol. 2013 Dec;246(12):915-26. doi: 10.1007/s00232-013-9593-0. J Membr Biol. 2013. PMID: 24077989 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of ammonia transport by the kidney Rh glycoproteins RhBG and RhCG.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Feb;290(2):F297-305. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00147.2005. Epub 2005 Aug 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16131648 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular physiology of the Rh ammonia transport proteins.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010 Sep;19(5):471-7. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32833bfa4e. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 20539225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The challenge of understanding ammonium homeostasis and the role of the Rh glycoproteins.Transfus Clin Biol. 2006 Mar-Apr;13(1-2):139-46. doi: 10.1016/j.tracli.2006.02.008. Epub 2006 Mar 29. Transfus Clin Biol. 2006. PMID: 16564724 Review.
Cited by
-
Periplasmic vestibule plays an important role for solute recruitment, selectivity, and gating in the Rh/Amt/MEP superfamily.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 8;108(10):3970-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007240108. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21368153 Free PMC article.
-
Renal ammonia metabolism and transport.Compr Physiol. 2013 Jan;3(1):201-20. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c120010. Compr Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23720285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in the gills of the climbing perch, Anabas testudineus, is involved in both hypoosmotic regulation during seawater acclimation and active ammonia excretion during ammonia exposure.J Comp Physiol B. 2012 Aug;182(6):793-812. doi: 10.1007/s00360-012-0664-9. Epub 2012 Apr 22. J Comp Physiol B. 2012. PMID: 22526263
-
Prokaryotic ammonium transporters: what has three decades of research revealed?Microbiology (Reading). 2023 Jul;169(7):001360. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001360. Microbiology (Reading). 2023. PMID: 37450375 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of ammonia and ammonium transport by rhesus-associated glycoproteins.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 Dec 1;309(11):C747-58. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00085.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26354748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marini AM, Urrestarazu A, Beauwens R, Andre B. The Rh (rhesus) blood group polypeptides are related to NH4+ transporters. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:460–461. - PubMed
-
- Cartron JP. RH blood group system and molecular basis of Rh-deficiency. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 1999;12:655–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

