Implementation of a color-capable optofluidic microscope on a RGB CMOS color sensor chip substrate
- PMID: 20126679
- PMCID: PMC10578144
- DOI: 10.1039/b919004j
Implementation of a color-capable optofluidic microscope on a RGB CMOS color sensor chip substrate
Abstract
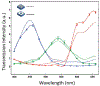
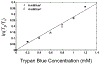
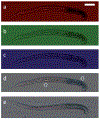
We report the implementation of a color-capable on-chip lensless microscope system, termed color optofluidic microscope (color OFM), and demonstrate imaging of double stained Caenorhabditis elegans with lacZ gene expression at a light intensity about 10 mW/cm(2).
Figures
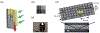
Similar articles
-
Lensless high-resolution on-chip optofluidic microscopes for Caenorhabditis elegans and cell imaging.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Aug 5;105(31):10670-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804612105. Epub 2008 Jul 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18663227 Free PMC article.
-
Optofluidic microscopy--a method for implementing a high resolution optical microscope on a chip.Lab Chip. 2006 Oct;6(10):1274-6. doi: 10.1039/b604676b. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Lab Chip. 2006. PMID: 17102839
-
The application of on-chip optofluidic microscopy for imaging Giardia lamblia trophozoites and cysts.Biomed Microdevices. 2009 Oct;11(5):951-8. doi: 10.1007/s10544-009-9312-x. Epub 2009 Apr 14. Biomed Microdevices. 2009. PMID: 19365730 Free PMC article.
-
Lensfree optofluidic microscopy and tomography.Ann Biomed Eng. 2012 Feb;40(2):251-62. doi: 10.1007/s10439-011-0385-3. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Ann Biomed Eng. 2012. PMID: 21887590 Review.
-
Label-free optical imaging of nonfluorescent molecules by stimulated radiation.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011 Dec;15(6):831-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.10.005. Epub 2011 Nov 4. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 22055495 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated cell viability assessment using a microfluidics based portable imaging flow analyzer.Biomicrofluidics. 2015 Apr 28;9(2):024123. doi: 10.1063/1.4919402. eCollection 2015 Mar. Biomicrofluidics. 2015. PMID: 26015835 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term imaging of three-dimensional hyphal development using the ePetri dish.Biomed Opt Express. 2024 Jun 17;15(7):4292-4299. doi: 10.1364/BOE.530483. eCollection 2024 Jul 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2024. PMID: 39022548 Free PMC article.
-
On-chip biomedical imaging.IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2013;6:29-46. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2012.2215847. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2013. PMID: 23558399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging without lenses: achievements and remaining challenges of wide-field on-chip microscopy.Nat Methods. 2012 Sep;9(9):889-95. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2114. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 22936170 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence microscopy imaging with a Fresnel zone plate array based optofluidic microscope.Lab Chip. 2011 Nov 7;11(21):3698-702. doi: 10.1039/c1lc20654k. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Lab Chip. 2011. PMID: 21935556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heng X, Erickson D, Baugh LR, Yaqoob Z, Sternberg PW, Psaltis D and Yang CH, Lab Chip, 2006, 6, 1274–1276. - PubMed
-
- Cui XQ, Lew M and Yang CH, Appl. Phys. Lett, 2008, 93,091113.
-
- Heng X, Cui XQ, Knapp DW, Wu JG, Yaqoob Z, McDowell EJ, Psaltis D and Yang CH, Opt. Express, 2006, 14, 10410–10425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

