Electrochemical sensing in paper-based microfluidic devices
- PMID: 20126688
- PMCID: PMC3065124
- DOI: 10.1039/b917150a
Electrochemical sensing in paper-based microfluidic devices
Abstract
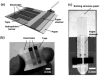
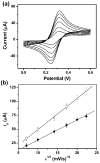
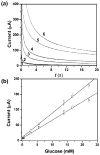
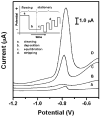
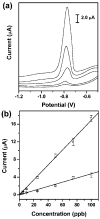
This paper describes the fabrication and the performance of microfluidic paper-based electrochemical sensing devices (we call the microfluidic paper-based electrochemical devices, microPEDs). The microPEDs comprise paper-based microfluidic channels patterned by photolithography or wax printing, and electrodes screen-printed from conducting inks (e.g., carbon or Ag/AgCl). We demonstrated that the microPEDs are capable of quantifying the concentrations of various analytes (e.g., heavy-metal ions and glucose) in aqueous solutions. This low-cost analytical device should be useful for applications in public health, environmental monitoring, and the developing world.
Figures
References
-
- Dungchai W, Chailapakul O, Henry CS. Anal Chem. 2009;81:5821–5826. - PubMed
-
- Hones J, Muller P, Surridge N. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2008;10:S10–S26.
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. WHO, WHO Press; Switzerland: 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

