Expression of TRF1, TRF2, TIN2, TERT, KU70, and BRCA1 proteins is associated with telomere shortening and may contribute to multistage carcinogenesis of gastric cancer
- PMID: 20127252
- PMCID: PMC11828133
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-010-0795-x
Expression of TRF1, TRF2, TIN2, TERT, KU70, and BRCA1 proteins is associated with telomere shortening and may contribute to multistage carcinogenesis of gastric cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Telomere dysfunction is believed to be a significant factor in carcinogenesis. To elucidate the carcinogenesis mechanism in gastric cancer, the expression of telomeric proteins and changes in telomere length were investigated during multistage carcinogenesis of gastric cancer.
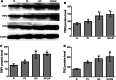
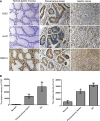
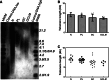
Methods: Tissue samples were obtained during surgical operations from the normal gastric mucosa of 10 patients, the precancerous lesions of 15 patients, the gastric cancer tissues (GC) of 20 patients, and of tumors due to gastric cancer with lymph node metastasis (GCLM) from 5 patients. The expression of TRF1, TRF2, and TIN2 proteins was measured by Western blotting, while the expression of TERT, KU70, and BRCA1 proteins was detected using the immunohistochemical method. The mean telomere length was determined by Southern blotting.
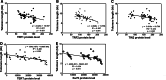
Results: Compared with normal gastric mucosa tissues, the expression of TRF1, TRF2, and TIN2 proteins was significantly higher in precancerous lesions, GC, and GCLM (P < 0.01). The expression of TRF1, TRF2, and TIN2 proteins was significantly higher in GC and GCLM than in precancerous lesions (P < 0.01). The expression of TERT and Ku70 proteins in precancerous lesions and GC tissues was significantly higher than that in normal gastric mucosa tissues (P < 0.01). The expression of TERT and Ku70 proteins in GC tissues was significantly higher than in precancerous lesions (P < 0.01). In normal gastric mucosa, the BRCA1 protein was primarily located in the cell nucleus. In precancerous lesions and GC, the expression of the BRCA1 protein was apparent in the cell cytoplasm. The mean telomere length in precancerous lesions, GC, and GCLM was significantly shorter than that in normal gastric mucosa tissues (P < 0.05). The mean telomere length in GC and GCLM was significantly shorter than that in precancerous lesions (P < 0.05). The mean telomere length in all tissue samples was inversely correlated with the level of TRF1, TRF2, TIN2, TERT, and Ku70 proteins.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the over-expression of telomeric proteins, TRF1, TRF2, TIN2, TERT, and Ku70, and the transposition of the BRCA1 protein may work together to reduce the telomere length in precancerous lesions and gastric cancer, and could contribute to the multistage carcinogenesis of gastric cancer. These findings offer new insight into the mechanism of carcinogenesis in gastric cancer.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

