Influence of image metrics when assessing image quality from a test object in cardiac X-ray systems
- PMID: 20127268
- PMCID: PMC3056969
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-009-9268-7
Influence of image metrics when assessing image quality from a test object in cardiac X-ray systems
Abstract
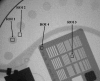
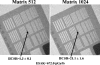
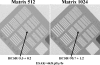
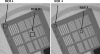
Modern fluoroscopic systems used for invasive cardiology typically acquire digital images in a 1,024 × 1,024 × 12 bits. These images are maintained in the original format while they remain on the imaging system itself. However, images are usually stored using a reduced 512 × 512 × 8-bits format. This paper presents a method for digital analysis of test objects images. The results obtained using image-intensifier and flat-detector systems are given for the original and reduced matrices. Images were acquired using a test object (TO) and a range of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) thicknesses from 4 to 28 cm. Adult patient protocols were evaluated for 16-28 cm of PMMA using the image-intensifier system. Pediatric protocols were evaluated for 4-16 cm of PMMA using the flat-detector system. The TO contains disks of various thicknesses to evaluate low contrast sensitivity and a bar pattern to evaluate high-contrast spatial resolution (HCSR). All available fluoroscopic and cine modes were evaluated. Entrance surface air kerma was also measured. Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was evaluated using regions of interest (ROI). HCSR was evaluated by comparing the statistical analysis of a ROI placed over the image of the bar pattern against a reference ROI. For both systems, an improvement of approximately 20% was observed for the SNR on the reduced matrices. However, the HCSR parameter was substantially lower in the reduced metrics. Cardiologists should consider the clinical influence of reduced spatial resolution when using the archived images.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Influence of image metrics when assessing image quality from a test object in cardiac X-ray systems: Part II.J Digit Imaging. 2012 Aug;25(4):537-41. doi: 10.1007/s10278-011-9448-0. J Digit Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22223157 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic flat panel detector versus image intensifier in cardiac imaging: dose and image quality.Phys Med Biol. 2005 Dec 7;50(23):5731-42. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/50/23/022. Epub 2005 Nov 23. Phys Med Biol. 2005. PMID: 16306664
-
Radiation dose and image quality for paediatric interventional cardiology.Phys Med Biol. 2008 Aug 7;53(15):4049-62. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/53/15/003. Epub 2008 Jul 8. Phys Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18612174
-
Dual-energy cardiac imaging: an image quality and dose comparison for a flat-panel detector and x-ray image intensifier.Phys Med Biol. 2007 Jan 7;52(1):183-96. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/52/1/012. Epub 2006 Dec 14. Phys Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17183135
-
[New realities in the modern X-ray technology].Med Tekh. 2003 Sep-Oct;(5):3-6. Med Tekh. 2003. PMID: 14603840 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Physical Image Quality Metrics for the Characterization of X-ray Systems Used in Fluoroscopy-Guided Pediatric Cardiac Interventional Procedures: A Systematic Review.Children (Basel). 2023 Nov 5;10(11):1784. doi: 10.3390/children10111784. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of image metrics when assessing image quality from a test object in cardiac X-ray systems: Part II.J Digit Imaging. 2012 Aug;25(4):537-41. doi: 10.1007/s10278-011-9448-0. J Digit Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22223157 Free PMC article.
-
Biplane interventional pediatric system with cone-beam CT: dose and image quality characterization for the default protocols.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016 Jul 8;17(4):357-376. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i4.5828. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27455474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Erickson BJ: Irreversible Compression of Medical Images. White Paper-Irreversible Compression of Medical Images. 2000. Available at: www.scarnet.org/WorkArea/showcontent.aspx?id=1208. Accessed 29 August 2009
-
- Brennecke R, Bürgel U, Simon R, Rippin G, Fritsch HP, Becker T, Nissen SE. American College of Cardiology European Society of Cardiology/International Study of Angiographic Data Compression Phase III: measurement of image quality differences at varying levels of data compression. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:1388–1397. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(99)00655-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kerensky RA, Cusma JT, Kubilis P, Simon R, Bashore TM, Hirshfeld JW, Jr, Holmes DR, Jr, Pepine CJ, Nissen SE. American College of Cardiology/European Society of Cardiology International Study of Angiographic Data Compression Phase I: the effect of lossy data compression on recognition of diagnostic features in digital coronary angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:1370–1379. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(99)00610-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

