Expression and prognostic relevance of CD44v6 in stage I non-small cell lung carcinoma
- PMID: 20127360
- PMCID: PMC11827903
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-010-0771-5
Expression and prognostic relevance of CD44v6 in stage I non-small cell lung carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Expression of CD44 and its variants has been shown to be relevant to tumor progression in various human malignancies. We evaluated the expression of CD44v6 in the primary lesions of stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and correlated the expression level to its prognosis.
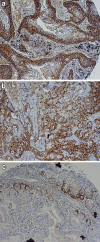
Methods: The expression of CD44v6, measured by immunohistochemistry, was assessed in the tumor specimens from 190 patients with stage I NSCLC. Each slide was assigned a score: the average of the score of tumor cells staining multiplied by the score of staining intensity. And depending on the cut-off score based on receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, the CD44v6 expression was categorized into high- and low-level groups, which were then correlated directly with the clinical outcomes.
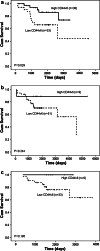
Results: The high expression of CD44v6 was detected more frequently in the squamous cell carcinoma (38 of 71 patients, 53.5%) than in the other types of carcinoma (p < 0.05). The Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that high level expression of CD44v6 indicated a better post-operative survival (p = 0.006), especially for stage IB disease (p = 0.049) and squamous cell carcinoma (p = 0.029). The multivariate analysis also confirmed that the expression of CD44v6 was an independent prognostic indicator (p = 0.011).
Conclusions: CD44v6 might be correlated with histogenesis of NSCLC, and its decreased expression may be an adverse prognostic indicator for the patients with stage I NSCLC, especially for those with stage IB diseases. Patients of this subgroup might need adjuvant therapy additionally.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Should patients with stage IB non-small cell lung cancer receive adjuvant chemotherapy? A comparison of survival between the 8th and 7th editions of the AJCC TNM staging system for stage IB patients.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb;145(2):463-469. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2801-7. Epub 2018 Nov 24. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30474757 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier 1 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241282080. doi: 10.1177/15330338241282080. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39360506 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) for the treatment of people with resected stage I to III non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR mutation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 May 27;5(5):CD015140. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015140.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40421698 Review.
-
Immunotherapy (excluding checkpoint inhibitors) for stage I to III non-small cell lung cancer treated with surgery or radiotherapy with curative intent.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 16;12(12):CD011300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011300.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 6;12:CD011300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011300.pub3. PMID: 29247502 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
Cited by
-
Alpha-CaMKII plays a critical role in determining the aggressive behavior of human osteosarcoma.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Apr;11(4):349-59. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0572. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23364534 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and association of CD44v6 with prognosis in T2-3N0M0 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2014 Feb;6(2):91-8. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.11.16. J Thorac Dis. 2014. PMID: 24605222 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of CD44 and CD44v6 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: meta-analysis.Tumour Biol. 2014 Aug;35(8):7383-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2150-3. Epub 2014 Jun 7. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24913707
-
Prognostic value of CD44 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Jun 15;7(7):3632-46. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25120740 Free PMC article.
-
Association of cancer stem cell markers genetic variants with gallbladder cancer susceptibility, prognosis, and survival.Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):1835-44. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3929-6. Epub 2015 Aug 30. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26318430
References
-
- ASCO (1997) Clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer. Adopted on May 16, by the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol 15(8):2996–3018 - PubMed
-
- Bains MS (1991) Surgical treatment of lung cancer. Chest 100(3):826–837 - PubMed
-
- Carter WG, Wayner EA (1988) Characterization of the class III collagen receptor, a phosphorylated, transmembrane glycoprotein expressed in nucleated human cells. J Biol Chem 263(9):4193–4201 - PubMed
-
- Coradini D, Zorzet S, Rossin R et al (2004) Inhibition of hepatocellular carcinomas in vitro and hepatic metastases in vivo in mice by the histone deacetylase inhibitor HA-But. Clin Cancer Res 10(14):4822–4830 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

