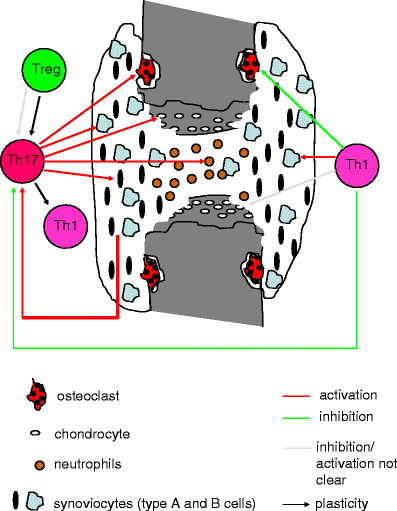
Th17 cytokines and arthritis
- PMID: 20127485
- PMCID: PMC2836464
- DOI: 10.1007/s00281-009-0189-9
Th17 cytokines and arthritis
Abstract
Th17 cells are implicated in human autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), although it has not been established whether this persistent destructive arthritis is driven by Th1 and/or Th17 cells. Interleukin-17A (IL-17A) contributes to the pathogenesis of arthritis as has been shown in several experimental arthritis models. Importantly, recent data from first clinical trials with anti-IL-17A antibody treatment in psoriatic arthritis patients and RA patients looks promising. This review summarizes the findings about the role of Th17 cells in arthritis and discusses the impact of the different Th17 cytokines in the pathogenesis of this disease. However, further studies are needed to unravel the interplay between IL-17A and other Th17 cytokines such as IL-17F, IL-22, and IL-21 in the pathoimmunological process of this crippling disease, in particular, whether regulating Th17 cell activity or specific combinations of Th17 cytokines will have additional value compared to neutralizing IL-17A activity alone. Moreover, tumor necrosis factor-positive Th17 cells are discussed as potential dangerous cells in driving persistent arthritis in human early RA.
Figures
References
-
- Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Joosten LA, Koenders MI, Devesa I, Roelofs MF, Radstake TR, Heuvelmans-Jacobs M, Akira S, Nicklin MJ, Ribeiro-Dias F, van den Berg WB. Stimulation of TLR2 and TLR4 differentially skews the balance of T cells in a mouse model of arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:205–216. doi: 10.1172/JCI32639. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical