Phospholipase A2 and its molecular mechanism after spinal cord injury
- PMID: 20127525
- PMCID: PMC9169014
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-010-8101-0
Phospholipase A2 and its molecular mechanism after spinal cord injury
Abstract
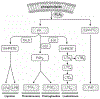
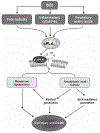
Phospholipases A(2) (PLA(2)s) are a diverse family of lipolytic enzymes which hydrolyze the acyl bond at the sn-2 position of glycerophospholipids to produce free fatty acids and lysophospholipids. These products are precursors of bioactive eicosanoids and platelet-activating factor which have been implicated in pathological states of numerous acute and chronic neurological disorders. To date, more than 27 isoforms of PLA(2) have been found in the mammalian system which can be classified into four major categories: secretory PLA(2), cytosolic PLA(2), Ca(2+)-independent PLA(2), and platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolases. Multiple isoforms of PLA(2) are found in the mammalian spinal cord. Under physiological conditions, PLA(2)s are involved in diverse cellular responses, including phospholipid digestion and metabolism, host defense, and signal transduction. However, under pathological situations, increased PLA(2) activity, excessive production of free fatty acids and their metabolites may lead to the loss of membrane integrity, inflammation, oxidative stress, and subsequent neuronal injury. There is emerging evidence that PLA(2) plays a key role in the secondary injury process after traumatic spinal cord injury. This review outlines the current knowledge of the PLA(2) in the spinal cord with an emphasis being placed on the possible roles of PLA(2) in mediating the secondary SCI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of secretory phospholipase a(2) in CNS inflammation: implications in traumatic spinal cord injury.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Jun;7(3):254-69. doi: 10.2174/187152708784936671. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18673210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipase A2 superfamily members play divergent roles after spinal cord injury.FASEB J. 2011 Dec;25(12):4240-52. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-183186. Epub 2011 Aug 25. FASEB J. 2011. PMID: 21868473 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phospholipase A2s and lipid mediators in secondary damage after spinal cord injury.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Jul;349(1):249-67. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1430-8. Epub 2012 May 13. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22581384 Review.
-
Involvement of cytosolic phospholipase A(2), calcium independent phospholipase A(2) and plasmalogen selective phospholipase A(2) in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric conditions.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(25):2746-63. doi: 10.2174/092986710791859289. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20586719 Review.
-
Phospholipase A2 biochemistry.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2009 Feb;23(1):49-59. doi: 10.1007/s10557-008-6132-9. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2009. PMID: 18931897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids improve the neurolipidome and restore the DHA status while promoting functional recovery after experimental spinal cord injury.J Neurotrauma. 2013 May 15;30(10):853-68. doi: 10.1089/neu.2012.2718. Epub 2013 Feb 6. J Neurotrauma. 2013. PMID: 23294084 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Cardiolipin-Targeted Tetrapeptide, SS-31, Exerts Neuroprotective Effects Within In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Spinal Cord Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 2;26(7):3327. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073327. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244206 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-modified hollow manganese dioxide nanoparticles loaded with resveratrol for the treatment of spinal cord injury.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):2498-2512. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2104957. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35903814 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 protein as a novel therapeutic target for spinal cord injury.Ann Neurol. 2014 May;75(5):644-58. doi: 10.1002/ana.24134. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Ann Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24623140 Free PMC article.
-
Further insight into molecular mechanism underlying thoracic spinal cord injury using bioinformatics methods.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Dec;12(6):7851-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4442. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26497545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kudo I, Murakami M (2002) Phospholipase A2 enzymes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 68–69:3–58 - PubMed
-
- Murakami M, Nakatani Y, Atsumi G, Inoue K, Kudo I (1997) Regulatory functions of phospholipase A2. Crit Rev Immunol 17:225–283 - PubMed
-
- Farooqui AA, Yang HC, Rosenberger TA, Horrocks LA (1997) Phospholipase A2 and its role in brain tissue. J Neurochem 69:889–901 - PubMed
-
- Bonventre JV (1996) Roles of phospholipases A2 in brain cell and tissue injury associated with ischemia and excitotoxicity. J Lipid Mediat Cell Signal 14:15–23 - PubMed
-
- Farooqui AA, Ong WY, Horrocks LA (2006) Inhibitors of brain phospholipase A2 activity: their neuropharmacological effects and therapeutic importance for the treatment of neurologic disorders. Pharmacol Rev 58:591–620 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

