Effects of perinatal protein deprivation and recovery on esophageal myenteric plexus
- PMID: 20128023
- PMCID: PMC2816267
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i5.563
Effects of perinatal protein deprivation and recovery on esophageal myenteric plexus
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate effects of pre- and postnatal protein deprivation and postnatal recovery on the myenteric plexus of the rat esophagus.
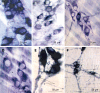
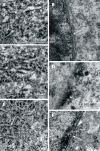
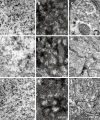
Methods: Three groups of young Wistar rats (aged 42 d) were studied: normal-fed (N42), protein-deprived (D42), and protein-recovered (R42). The myenteric neurons of their esophagi were evaluated by histochemical reactions for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH), nitrergic neurons (NADPH)-diaphorase and acetylcholinesterase (AChE), immunohistochemical reaction for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), and ultrastructural analysis by transmission electron microscopy.
Results: The cytoplasms of large and medium neurons from the N42 and R42 groups were intensely reactive for NADH. Only a few large neurons from the D42 group exhibited this aspect. NADPH detected in the D42 group exhibited low reactivity. The AChE reactivity was diffuse in neurons from the D42 and R42 groups. The density of large and small varicosities detected by immunohistochemical staining of VIP was low in ganglia from the D42 group. In many neurons from the D42 group, the double membrane of the nuclear envelope and the perinuclear cisterna were not detectable. NADH and NADPH histochemistry revealed no group differences in the profile of nerve cell perikarya (ranging from 200 to 400 microm(2)).
Conclusion: Protein deprivation causes a delay in neuronal maturation but postnatal recovery can almost completely restore the normal morphology of myenteric neurons.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of combined pre- and post-natal protein deprivation on the myenteric plexus of the esophagus of weanling rats: a histochemical, quantitative and ultrastructural study.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jul 14;13(26):3598-604. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3598. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17659710 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of pre- and postnatal protein deprivation and postnatal refeeding on myenteric neurons of the rat small intestine: a quantitative morphological study.Auton Neurosci. 2006 Jun 30;126-127:277-84. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2006.03.003. Epub 2006 May 18. Auton Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16713368
-
Distribution of myenteric NO neurons along the guinea-pig esophagus.J Auton Nerv Syst. 1998 Dec 11;74(2-3):91-9. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1838(98)00131-3. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1998. PMID: 9915623
-
Myenteric nitrergic neurons along the rat esophagus: evidence for regional and strain differences in age-related changes.Histochem Cell Biol. 2003 May;119(5):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s00418-003-0526-3. Epub 2003 Apr 30. Histochem Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12721679
-
The effect of age on colocalization of acetylcholinesterase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase staining in enteric neurons in an experimental model.J Pediatr Surg. 2007 Feb;42(2):300-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2006.10.031. J Pediatr Surg. 2007. PMID: 17270539
Cited by
-
Association between jejunal remodeling in fasting rats and hypersensitivity of intestinal afferent nerves to mechanical stimulation.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2024 Feb;23(1):73-86. doi: 10.1007/s10237-023-01758-7. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2024. PMID: 37548873
-
Expression of the P2X₂ receptor in different classes of ileum myenteric neurons in the female obese ob/ob mouse.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Sep 14;18(34):4693-703. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4693. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23002338 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of protein deprivation and re-feeding on P2X2 receptors in enteric neurons.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Aug 7;16(29):3651-63. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i29.3651. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20677337 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with low doses of aspirin during chronic phase of experimental Chagas' disease increases oesophageal nitrergic neuronal subpopulation in mice.Int J Exp Pathol. 2017 Dec;98(6):356-362. doi: 10.1111/iep.12259. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Int J Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 29349896 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ischemia and reperfusion on P2X2 receptor expressing neurons of the rat ileum enteric nervous system.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Aug;56(8):2262-75. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1588-z. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21409380
References
-
- Castelucci P, de Souza RR, de Angelis RC, Furness JB, Liberti EA. Effects of pre- and postnatal protein deprivation and postnatal refeeding on myenteric neurons of the rat large intestine: a quantitative morphological study. Cell Tissue Res. 2002;310:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Brandão MCS, De Angelis RC, De-Souza RR, Fróes LB, Liberti EA. Effects of pre- and postnatal protein energy deprivation on the myenteric plexus of the small intestine: a morphometric study in weanling rats. Nut Res. 2003;23:215–223.
-
- Gomes OA, Castelucci P, de Vasconcellos Fontes RB, Liberti EA. Effects of pre- and postnatal protein deprivation and postnatal refeeding on myenteric neurons of the rat small intestine: a quantitative morphological study. Auton Neurosci. 2006;126-127:277–284. - PubMed
-
- Mello ST, Liberti EA, Sant'Ana DMG, Miranda Neto MH. The myenteric plexus in the duodenum of rats with deficiency of protein and vitamin B complex: a morpho-quantitative study. Acta Scientiarum. 2004;26:251–256.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

