Characterization of microRNAs involved in embryonic stem cell states
- PMID: 20128659
- PMCID: PMC3128320
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2009.0426
Characterization of microRNAs involved in embryonic stem cell states
Abstract
Studies of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) reveal that these cell lines can be derived from differing stages of embryonic development. We analyzed common changes in the expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) and mRNAs in 9 different human ESC (hESC) lines during early commitment and further examined the expression of key ESCenriched miRNAs in earlier developmental states in several species. We show that several previously defined hESC-enriched miRNA groups (the miR-302, -17, and -515 families, and the miR-371-373 cluster) and several other hESC-enriched miRNAs are down-regulated rapidly in response to differentiation. We further found that mRNAs up-regulated upon differentiation are enriched in potential target sites for these hESC-enriched miRNAs. Interestingly, we also observed that the expression of ESC-enriched miRNAs bearing identical seed sequences changed dynamically while the cells transitioned through early embryonic states. In human and monkey ESCs, as well as human-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), the miR-371-373 cluster was consistently up-regulated, while the miR-302 family was mildly down-regulated when the cells were chemically treated to regress to an earlier developmental state. Similarly, miR-302b, but not mmu-miR-295, was expressed at higher levels in murine epiblast stem cells (mEpiSC) as compared with an earlier developmental state, mouse ESCs. These results raise the possibility that the relative expression of related miRNAs might serve as diagnostic indicators in defining the developmental state of embryonic cells and other stem cell lines, such as iPSCs. These data also raise the possibility that miRNAs bearing identical seed sequences could have specific functions during separable stages of early embryonic development.
Figures
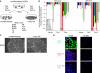
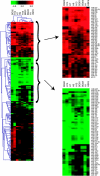

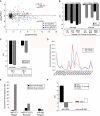
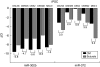
Similar articles
-
Distinct MicroRNA Expression Signatures of Porcine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells under Mouse and Human ESC Culture Conditions.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 6;11(7):e0158655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158655. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27384321 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of microRNAs regulated by activin A in human embryonic stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2010 Jan 1;109(1):93-102. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22385. J Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19885849
-
Embryonic stem cell microRNAs: defining factors in induced pluripotent (iPS) and cancer (CSC) stem cells?Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Sep;4(3):168-77. doi: 10.2174/157488809789057400. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19492978 Review.
-
Changes in microRNA expression during differentiation of embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells to definitive endoderm.Gene Expr Patterns. 2015 Sep-Nov;19(1-2):70-82. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Gene Expr Patterns. 2015. PMID: 26277621 Free PMC article.
-
The Key Role of MicroRNAs in Self-Renewal and Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6285. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176285. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32877989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of CDS-located miRNA target sites suggests that they can effectively inhibit translation.Genome Res. 2013 Apr;23(4):604-15. doi: 10.1101/gr.139758.112. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23335364 Free PMC article.
-
Developmentally programmed 3' CpG island methylation confers tissue- and cell-type-specific transcriptional activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 May;33(9):1845-58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01124-12. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23459939 Free PMC article.
-
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway regulates the expression of the miR-302 cluster in mouse ESCs and P19 cells.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 10;8(9):e75315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075315. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040406 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of ULK1 by microRNA-372 inhibits the survival of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.Cancer Sci. 2017 Sep;108(9):1811-1819. doi: 10.1111/cas.13315. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28677209 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of microRNA-302a inhibited the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by regulation of the MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):4481-91. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomson JA. Itskovitz-Eldor J. Shapiro SS. Waknitz MA. Swiergiel JJ. Marshall VS. Jones JM. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Evans MJ. Kaufman MH. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292:154–156. - PubMed
-
- Klimanskaya I. Rosenthal N. Lanza R. Derive and conquer: sourcing and differentiating stem cells for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:131–142. - PubMed
-
- Spagnoli FM. Hemmati-Brivanlou A. Guiding embryonic stem cells towards differentiation: lessons from molecular embryology. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16:469–475. - PubMed
-
- Maherali N. Sridharan R. Xie W. Utikal J. Eminli S. Arnold K. Stadtfeld M. Yachechko R. Tchieu J. Jaenisch R. Plath K. Hochedlinger K. Directly reprogrammed fibroblasts show global epigenetic remodeling and widespread tissue contribution. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:55–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

