Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 are both required for ischaemic excitotoxicity
- PMID: 20128796
- PMCID: PMC2839275
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00595.x
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 are both required for ischaemic excitotoxicity
Abstract
Background and purpose: Although both microsomal prostaglandin E synthase (mPGES)-1 and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 are critical factors in stroke injury, but the interactions between these enzymes in the ischaemic brain is still obscure. This study examines the hypothesis that mPGES-1 activity is required for COX-2 to cause neuronal damage in ischaemic injury.
Experimental approach: We used a glutamate-induced excitotoxicity model in cultures of rat or mouse hippocampal slices and a mouse middle cerebral artery occlusion-reperfusion model in vivo. The effect of a COX-2 inhibitor on neuronal damage in mPGES-1 knockout (KO) mice was compared with that in wild-type (WT) mice.
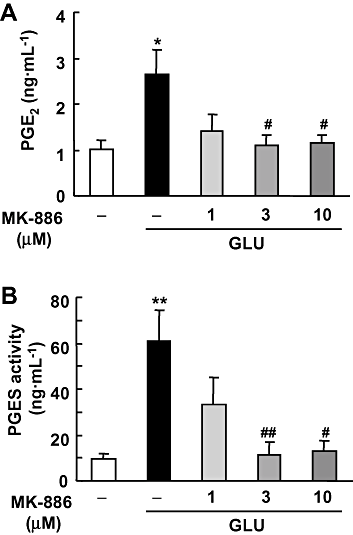
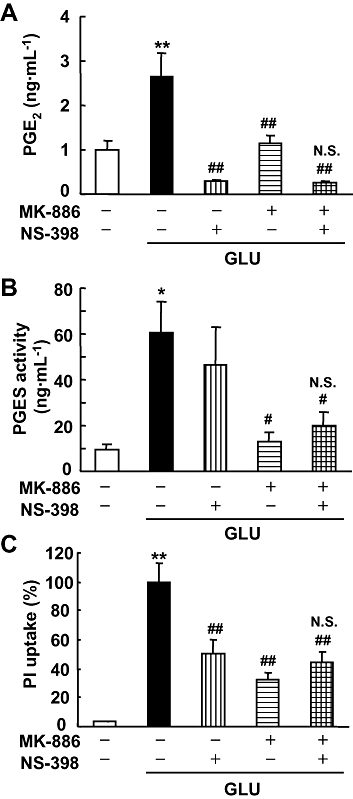
Key results: In rat hippocampal slices, glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, as well as prostaglandin (PG) E(2) production and PGES activation, was significantly attenuated by either MK-886 or NS-398, inhibitors of mPGES-1 and COX-2 respectively; however, co-application of these inhibitors had neither an additive nor a synergistic effect. The protective effect of NS-398 on the excitotoxicity observed in WT slices was completely abolished in mPGES-1 KO slices, which showed less excitotoxicity than WT slices. In the transient focal ischaemia model, mPGES-1 and COX-2 were co-localized in the infarct region of the cortex. Injection of NS-398 reduced not only ischaemic PGE(2) production, but also ischaemic injuries in WT mice, but not in mPGES-1 KO mice, which showed less dysfunction than WT mice.
Conclusion and implications: Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 and COX-2 are co-induced by excess glutamate in ischaemic brain. These enzymes are co-localized and act together to exacerbate stroke injury, by excessive PGE(2) production.
Figures





References
-
- Ahmad AS, Ahmad M, de Brum-Fernandes AJ, Doré S. Prostaglandin EP4 receptor agonist protects against acute neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 2005;1066:71–77. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad AS, Saleem S, Ahmad M, Doré S. Prostaglandin EP1 receptor contributes to excitotoxicity and focal ischemic brain damage. Toxicol Sci. 2006;89:265–270. - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM, Mirro R, Busija DW, Leffler CW. post-ischaemic generation of superoxide anion by newborn pig brain. Am J Physiol. 1988;255:H401–H403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

