Substance P and glutamate receptor antagonists improve the anti-arthritic actions of dexamethasone in rats
- PMID: 20128799
- PMCID: PMC2829221
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00586.x
Substance P and glutamate receptor antagonists improve the anti-arthritic actions of dexamethasone in rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Current single drug treatments for rheumatoid arthritis have problems of limited efficacy and/or high toxicity. This study investigates the benefits of individual and combined treatments with dexamethasone and substance P and glutamate receptor antagonists in a rat model of arthritis.
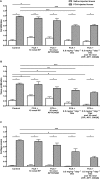
Experimental approach: Arthritis was induced in rats by unilateral intra-articular injection of Freund's complete adjuvant. Separate groups of rats were subjected to the following treatments 15 min before induction of arthritis: (i) control with no drug treatment; (ii) single intra-articular injection of a NK(1) receptor antagonist RP67580; (iii) single intra-articular injection of a NMDA receptor antagonist AP7 plus a non-NMDA receptor antagonist CNQX; (iv) daily oral dexamethasone; and (v) combined treatment with dexamethasone and all of the above receptor antagonists. Knee joint allodynia, swelling, hyperaemia and histological changes were examined over a period of 7 days.
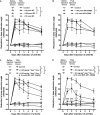
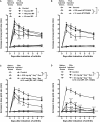
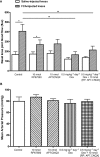
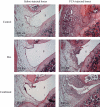
Key results: Treatment with dexamethasone suppressed joint swelling, hyperaemia and histological changes that include polymorphonuclear cell infiltration, synovial tissue proliferation and cartilage erosion in the arthritic rat knees. Treatment with RP67580 or AP7 plus CNQX did not attenuate hyperaemia or histological changes, but reduced joint allodynia and swelling. Co-administration of dexamethasone with these receptor antagonists produced greater inhibition on joint allodynia and swelling than their individual effects.
Conclusions and implications: The data suggest substance P and glutamate contribute to arthritic pain and joint swelling. The efficacy of dexamethasone in reducing arthritic pain and joint swelling can be improved by co-administration of substance P and glutamate receptor antagonists.
Figures
References
-
- Arend WP. The pathophysiology and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:595–597. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Rustioni A. Coexistence of glutamate and substance P in dorsal root ganglion neurons of the rat and monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1988;277:302–312. - PubMed
-
- Bendele AM. Animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. J Musculoskelet Neuron Interact. 2001;1:377–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

