Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection
- PMID: 20128800
- PMCID: PMC2828015
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00486.x
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection
Abstract
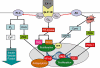
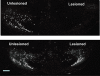
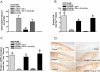
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is a relatively recently discovered molecule originating in the so-called L-cells of the intestine. The peptide has insulinotrophic properties and it is this characteristic that has predominantly been investigated. This has led to the use of the GLP-1-like peptide exendin-4 (EX-4), which has a much longer plasma half-life than GLP-1 itself, being used in the treatment of type II diabetes. The mode of action of this effect appears to be a reduction in pancreatic apoptosis, an increase in beta cell proliferation or both. Thus, the effects of GLP-1 receptor stimulation are not based upon insulin replacement but an apparent repair of the pancreas. Similar data suggest that the same effects may occur in other peripheral tissues. More recently, the roles of GLP-1 and EX-4 have been studied in nervous tissue. As in the periphery, both peptides appear to promote cellular growth and reduce apoptosis. In models of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and peripheral neuropathy, stimulation of the GLP-1 receptor has proved to be highly beneficial. In the case of Parkinson's disease this effect is evident after the neurotoxic lesion is established, suggesting real potential for therapeutic use. In the present review we examine the current status of the GLP-1 receptor and its potential as a therapeutic target.
Figures
References
-
- Abuirmeileh A, Harkavyi A, Kingsbury A, Lever R, Whitton PS. The CRF-like peptide urocortin greatly attenuates loss of extracellular striatal dopamine in rat models of Parkinson's disease by activating CRF1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;604:45–50. - PubMed
-
- Baggio LL, Huang Q, Brown TJ, Drucker DJ. A recombinant human glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1-albumin protein (albugon) mimics peptidergic activation of GLP-1 receptor-dependent pathways coupled with satiety, gastrointestinal motility, and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes. 2004;53:2492–2500. - PubMed
-
- Bertilsson G, Patrone C, Zachrisson O, Andersson A, Dannaeus K, Heidrich J, et al. Peptide hormone exendin-4 stimulates subventricular zone neurogenesis in the adult rodent brain and induces recovery in an animal model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci Res. 2008;86:326–338. - PubMed
-
- Buteau J, El-Assaad W, Rhodes CJ, Rosenberg L, Joly E, Prentki M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 prevents beta cell glucolipotoxicity. Diabetologia. 2004;47:806–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

