Cilostazol is anti-inflammatory in BV2 microglial cells by inactivating nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinases
- PMID: 20128801
- PMCID: PMC2848931
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00615.x
Cilostazol is anti-inflammatory in BV2 microglial cells by inactivating nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinases
Abstract
Background and purpose: Cilostazol is a specific inhibitor of 3'-5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) phosphodiesterase, which is widely used to treat ischemic symptoms of peripheral vascular disease. Although cilostazol has been shown to exhibit vasodilator properties as well as antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory effects, its cellular mechanism in microglia is unknown. In the present study, we assessed the anti-inflammatory effect of cilostazol on the production of pro-inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated murine BV2 microglia.
Experimental approach: We examined the effects of cilostazol on LPS-induced nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation and phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs).
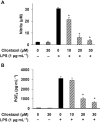
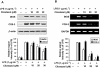
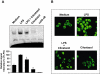
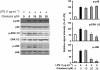
Key results: Cilostazol suppressed production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and the proinflammatory cytokines, interleukin-1 (IL-1), tumour necrosis factor-alpha, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), in a concentration-dependent manner. Inhibitory effects of cilostazol were not affected by treatment with an adenylate cyclase inhibitor, SQ 22536, indicating that these actions of cilostazol were cAMP-independent. Cilostazol significantly inhibited the DNA binding and transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB. Moreover, cilostazol blocked signalling upstream of NF-kappaB activation by inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), but without affecting the activity of p38 MAPK.
Conclusion and implications: Our results demonstrate that suppression of the NF-kappaB, ERK, JNK signalling pathways may inhibit LPS-induced NO and PGE(2) production. Therefore, cilostazol may have therapeutic potential for neurodegenerative diseases by inhibiting pro-inflammatory mediators and cytokine production in activated microglia.
Figures


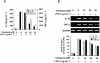

Similar articles
-
Naringenin attenuates the release of pro-inflammatory mediators from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia by inactivating nuclear factor-κB and inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinases.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Jul;30(1):204-10. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.979. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22552813
-
Hexane fraction of Zingiberis Rhizoma Crudus extract inhibits the production of nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells via the NF-kappaB pathway.Food Chem Toxicol. 2009 Jun;47(6):1190-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2009.02.012. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19233241
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Migratory Activities of Isoquinoline-1-Carboxamide Derivatives in LPS-Treated BV2 Microglial Cells via Inhibition of MAPKs/NF-κB Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 27;21(7):2319. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072319. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32230861 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic AMP: a selective modulator of NF-κB action.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Dec;68(23):3823-41. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0757-8. Epub 2011 Jul 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21744067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Updated Review on the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Phyllanthus Genus.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Apr 24:e202402483. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202402483. Online ahead of print. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 40271556 Review.
Cited by
-
Oleifolioside A, a New Active Compound, Attenuates LPS-Stimulated iNOS and COX-2 Expression through the Downregulation of NF-κB and MAPK Activities in RAW 264.7 Macrophages.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:637512. doi: 10.1155/2012/637512. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22911495 Free PMC article.
-
Ibudilast, a pharmacologic phosphodiesterase inhibitor, prevents human immunodeficiency virus-1 Tat-mediated activation of microglial cells.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 8;6(4):e18633. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018633. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21494611 Free PMC article.
-
Model difference in the effect of cilostazol on the development of experimental pulmonary hypertension in rats.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Nov 20;21(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01710-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34801000 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis reveals Cilostazol's role in ameliorating cardiovascular disease: Inhibition of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and reduction of endothelial cell reactive oxygen species production.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 3;10(7):e29194. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29194. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38601627 Free PMC article.
-
Evodiamine Inhibits Zymosan-Induced Inflammation In Vitro and In Vivo: Inactivation of NF-κB by Inhibiting IκBα Phosphorylation.Inflammation. 2017 Jun;40(3):1012-1027. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0546-0. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 28337636
References
-
- Akassoglou K, Bauer J, Kassiotis G, Pasparakis M, Lassmann H, Kollias G, et al. Oligodendrocyte apoptosis and primary demyelination induced by local TNF/p55TNF receptor signaling in the central nervous system of transgenic mice: models for multiple sclerosis with primary oligodendrogliopathy. Am J Pathol. 1998;153:801–813. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AS., Jr. The NF-kappaB and I-kappaB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–683. - PubMed
-
- Bauer MK, Lieb K, Schulze-Osthoff K, Berger M, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Bauer J, et al. Expression and regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in rat microglia. Eur J Biochem. 1997;243:726–731. - PubMed
-
- Boka G, Anglade P, Wallach D, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y, Hirsch EC. Immunocytochemical analysis of tumor necrosis factor and its receptors in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1994;172:151–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

