Pharmacological stimulation and inhibition of insulin secretion in mouse islets lacking ATP-sensitive K+ channels
- PMID: 20128805
- PMCID: PMC2828030
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00588.x
Pharmacological stimulation and inhibition of insulin secretion in mouse islets lacking ATP-sensitive K+ channels
Abstract
Background and purpose: ATP-sensitive potassium channels (K(ATP) channels) in beta cells are a major target for insulinotropic drugs. Here, we studied the effects of selected stimulatory and inhibitory pharmacological agents in islets lacking K(ATP) channels.
Experimental approach: We compared insulin secretion (IS) and cytosolic calcium ([Ca(2+)](c)) changes in islets isolated from control mice and mice lacking sulphonylurea receptor1 (SUR1), and thus K(ATP) channels in their beta cells (Sur1KO).
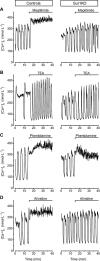
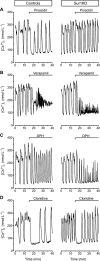
Key results: While similarly increasing [Ca(2+)](c) and IS in controls, agents binding to site A (tolbutamide) or site B (meglitinide) of SUR1 were ineffective in Sur1KO islets. Of two non-selective blockers of potassium channels, quinine was inactive, whereas tetraethylammonium was more active in Sur1KO compared with control islets. Phentolamine, efaroxan and alinidine, three imidazolines binding to K(IR)6.2 (pore of K(ATP) channels), stimulated control islets, but only phentolamine retained weaker stimulatory effects on [Ca(2+)](c) and IS in Sur1KO islets. Neither K(ATP) channel opener (diazoxide, pinacidil) inhibited Sur1KO islets. Calcium channel blockers (nimodipine, verapamil) or diphenylhydantoin decreased [Ca(2+)](c) and IS in both types of islets, verapamil and diphenylhydantoin being more efficient in Sur1KO islets. Activation of alpha(2)-adrenoceptors or dopamine receptors strongly inhibited IS while partially (clonidine > dopamine) lowering [Ca(2+)](c) (control > Sur1KO islets).
Conclusions and implications: Those drugs retaining effects on IS in islets lacking K(ATP) channels, also affected [Ca(2+)](c), indicating actions on other ionic channels. The greater effects of some inhibitors in Sur1KO than in control islets might be relevant to medical treatment of congenital hyperinsulinism caused by inactivating mutations of K(ATP) channels.
Figures
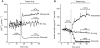
Similar articles
-
Both triggering and amplifying pathways contribute to fuel-induced insulin secretion in the absence of sulfonylurea receptor-1 in pancreatic beta-cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 30;279(31):32316-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402076200. Epub 2004 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15175349
-
ATP-sensitive potassium channels and efaroxan-induced insulin release in the electrofusion-derived BRIN-BD11 beta-cell line.Diabetes. 1999 Dec;48(12):2349-57. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.48.12.2349. Diabetes. 1999. PMID: 10580423
-
Glucose stimulates Ca2+ influx and insulin secretion in 2-week-old beta-cells lacking ATP-sensitive K+ channels.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jan 19;282(3):1747-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609875200. Epub 2006 Nov 30. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17138557
-
ATP-regulated potassium channels and voltage-gated calcium channels in pancreatic alpha and beta cells: similar functions but reciprocal effects on secretion.Diabetologia. 2014 Sep;57(9):1749-61. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3279-8. Epub 2014 Jun 7. Diabetologia. 2014. PMID: 24906950 Review.
-
Studies of first phase insulin secretion using imposed plasma membrane depolarization.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2011 Jan 1;3(2):662-79. doi: 10.2741/s179. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196404 Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine modulates insulin release and is involved in the survival of rat pancreatic beta cells.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 17;10(4):e0123197. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123197. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25886074 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that the multiflorine-derived substituted quinazolidine 55P0251 augments insulin secretion and lowers blood glucose via antagonism at α2 -adrenoceptors in mice.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020 Mar;22(3):290-302. doi: 10.1111/dom.13895. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020. PMID: 31608542 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of antihyperglycaemic action of efaroxan in mice: time for reappraisal of α2A-adrenergic antagonism in the treatment of type 2 diabetes?Diabetologia. 2012 Nov;55(11):3071-82. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2679-x. Epub 2012 Aug 18. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22898767
-
Quinine: rediscovery of an old glucose-lowering drug.Diabetologia. 2025 Jun;68(6):1355-1356. doi: 10.1007/s00125-025-06416-4. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Diabetologia. 2025. PMID: 40131420 No abstract available.
-
BetaBuddy: An automated end-to-end computer vision pipeline for analysis of calcium fluorescence dynamics in β-cells.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 15;19(3):e0299549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299549. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38489336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bryan J, Crane A, Vila-Carriles WH, Babenko AP, Aguilar-Bryan L. Insulin secretagogues, sulfonylurea receptors and K(ATP) channels. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11:2699–2716. - PubMed
-
- Bryan J, Muñoz A, Zhang X, Düfer M, Drews G, Krippeit-Drews P, et al. ABCC8 and ABCC9: ABC transporters that regulate K+ channels. Pflugers Arch. 2007;453:703–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

