Lack of effect of the alpha2C-adrenoceptor Del322-325 polymorphism on inhibition of cyclic AMP production in HEK293 cells
- PMID: 20128806
- PMCID: PMC2829208
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00584.x
Lack of effect of the alpha2C-adrenoceptor Del322-325 polymorphism on inhibition of cyclic AMP production in HEK293 cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: The alpha(2C)-adrenoceptor has multiple functions, including inhibiting release of noradrenaline from presynaptic nerve terminals. A human alpha(2C) polymorphism, Del322-325, a potential risk factor for heart failure, has been reported to exhibit reduced signalling in CHO cells. To further understand the role of the Del322-325 polymorphism on receptor signalling, we attempted to replicate and further study the reduced signalling in HEK293 cells.
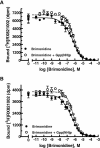
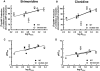
Experimental approach: Human alpha(2C) wild-type (WT) and Del322-325 adrenoceptors were stably transfected into HEK293 cells. Radioligand binding was performed to determine affinities for both receptors. In intact cells, inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP production by WT and Del322-325 clones with a range of receptor densities (200-2320 fmol.mg(-1) protein) was measured following agonist treatment.
Key results: Noradrenaline, brimonidine and clonidine exhibited similar binding affinities for WT and Del322-325. Brimonidine and clonidine also had similar efficacies and potencies for both receptors for the inhibition of cyclic AMP production at all receptor densities tested. A linear regression analysis comparing efficacy and potency with receptor expression levels showed no differences in slopes between WT and Del322-325.
Conclusions and implications: The alpha(2C) WT and Del322-325 adrenoceptors exhibited similar binding properties. Additionally, inhibition of cyclic AMP production by Del322-325 was similar to that of WT over a range of receptor densities. Therefore, in intact HEK293 cells, the alpha(2C)-Del322-325 polymorphism does not exhibit reduced signalling to adenylyl cyclase and may not represent a clinically important phenotype.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alpha2-adrenoceptor regulation of adenylyl cyclase in CHO cells: dependence on receptor density, receptor subtype and current activity of adenylyl cyclase.Eur J Pharmacol. 1997 Sep 17;335(1):53-63. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(97)01154-0. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9371546
-
Alpha2C-adrenoceptors mediate inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP production in rat striatum.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997 Dec 15;52(2):228-34. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(97)00257-x. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997. PMID: 9495543
-
Functional alpha2C-adrenoceptors in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 May 7;372(1):109-15. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00190-9. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10374721
-
Comparative pharmacology of adrenergic alpha(2C) receptors coupled to Ca(2+) signaling through different Galpha proteins.Neurochem Int. 2009 Dec;55(7):467-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.04.015. Epub 2009 May 6. Neurochem Int. 2009. PMID: 19426776
-
Signalling of Adrenoceptors: Canonical Pathways and New Paradigms.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;285:147-184. doi: 10.1007/164_2023_704. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38227198 Review.
Cited by
-
Common α2A and α2C adrenergic receptor polymorphisms do not affect plasma membrane trafficking.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;387(6):569-579. doi: 10.1007/s00210-014-0972-6. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24643471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler CH, Meller E, Goldstein M. Receptor reserve at the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor in the rat cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987;240:508–515. - PubMed
-
- Agneter E, Singer EA, Sauermann W, Feuerstein TJ. The slope parameter of concentration-response curves used as a touchstone for the existence of spare receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1997;356:283–292. - PubMed
-
- Brede M, Wiesmann F, Jahns R, Hadamek K, Arnolt C, Neubauer S, et al. Feedback inhibition of catecholamine release by two different alpha2-adrenoceptor subtypes prevents progression of heart failure. Circulation. 2002;106:2491–2496. - PubMed
-
- Bristow MR. Why does the myocardium fail? Insights from basic science. Lancet. 1998;352(Suppl. 1):SI8–SI14. - PubMed
-
- Bucheler MM, Hadamek K, Hein L. Two alpha(2)-adrenergic receptor subtypes, alpha(2A) and alpha(2C), inhibit transmitter release in the brain of gene-targeted mice. Neuroscience. 2002;109:819–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

