Stimulation of angiotensin AT2 receptors by the non-peptide agonist, Compound 21, evokes vasodepressor effects in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 20128808
- PMCID: PMC2828034
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00575.x
Stimulation of angiotensin AT2 receptors by the non-peptide agonist, Compound 21, evokes vasodepressor effects in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Angiotensin type 2 receptor (AT(2) receptor) stimulation evokes vasodilator effects in vitro and in vivo that oppose the vasoconstrictor effects of angiotensin type 1 receptors (AT(1) receptors). Recently, a novel non-peptide AT(2) receptor agonist, Compound 21, was described, which exhibited high AT(2) receptor selectivity.
Experimental approach: Functional cardiovascular effects of the drug candidate Compound 21 were assessed, using mouse isolated aorta and rat mesenteric arteries in vitro and in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR).
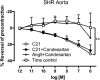
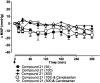
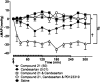
Key results: Compound 21 evoked dose-dependent vasorelaxations in aortic and mesenteric vessels, abolished by the AT(2) receptor antagonist, PD123319. In vivo, Compound 21 administered alone, at doses ranging from 50 to 1000 ng.kg(-1).min(-1) over 4 h did not decrease blood pressure in conscious normotensive Wistar-Kyoto rats or SHR. However, when given in combination with the AT(1) receptor antagonist, candesartan, Compound 21 (300 ng.kg(-1).min(-1)) lowered blood pressure in SHR only. Further analysis in separate groups of conscious SHR revealed that, at a sixfold lower dose, Compound 21 (50 ng.kg(-1).min(-1)) still evoked a significant depressor response in adult SHR ( approximately 30 mmHg) when combined with different doses of candesartan (0.01 or 0.1 mg.kg(-1)). Moreover, the Compound 21-evoked depressor effect was abolished when co-infused (50 microg.kg(-1).min(-1) for 2 h) with the AT(2) receptor antagonist PD123319.
Conclusion and implications: Collectively, our results indicate that acute administration of Compound 21 evoked blood pressure reductions via AT(2) receptor stimulation. Thus Compound 21 can be considered an excellent drug candidate for further study of AT(2) receptor function in cardiovascular disease.
Figures



References
-
- Barber MN, Sampey DB, Widdop RE. AT2 receptor stimulation enhances antihypertensive effect of AT1 receptor antagonist in hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1999;34:1112–1116. - PubMed
-
- Carey RM. Update on the role of the AT(2) receptor. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2005;14:67–71. - PubMed
-
- Carey RM, Howell NL, Jin X-H, Siragy HM. Angiotensin type 2 receptor-mediated hypotension in angiotensin type-1 receptor-blocked rats. Hypertension. 2001;38:1272–1277. - PubMed
-
- Cosentino F, Savoia C, De Paolis P, Francia P, Russo A, Maffei A, et al. Angiotensin II type 2 receptors contribute to vascular responses in spontaneously hypertensive rats treated with angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists. Am J Hypertens. 2005;18:493–499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

