Functional interactions between 5-HT2A and presynaptic 5-HT1A receptor-based responses in mice genetically deficient in the serotonin 5-HT transporter (SERT)
- PMID: 20128812
- PMCID: PMC2829213
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00578.x
Functional interactions between 5-HT2A and presynaptic 5-HT1A receptor-based responses in mice genetically deficient in the serotonin 5-HT transporter (SERT)
Abstract
Background and purpose: Despite decreased presynaptic 5-HT(1A) and altered 5-HT(2A) receptor function in genetically-deficient serotonin (5-HT) transporter (SERT) mice, the 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist N-[2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-N-2-pyridinylcyclohexanecarboxamide maleate salt (WAY 100635) still induced head twitches in these mice, a well-established 5-HT(2A) receptor-mediated response.
Experimental approach: Interactions between 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(2A) receptors were assessed using the head-twitch response following 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(2A) receptor agonists and antagonists in SERT wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/-), and knockout (-/-) mice. The role of brain 5-HT availability in WAY 100635 induced head twitches was also examined.
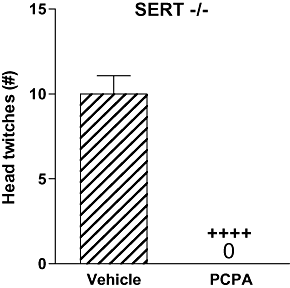
Key results: WAY 100635 induced head twitches in a SERT gene-dose dependent manner, inducing 5-fold more head twitches in SERT -/- versus SERT +/+ mice. In SERT -/- mice, inhibition of 5-HT synthesis with p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA) markedly depleted tissue 5-HT in all five brain areas examined and abolished WAY 100635 induced head twitches. Further, the selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitor fluvoxamine increased WAY 100635 induced head twitches in SERT +/+ and +/- mice. Head twitches following the 5-HT(2A) receptor agonist (+/-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane (DOI) were robust in SERT +/+ and +/- mice but much reduced in SERT -/- mice. DOI-induced head twitches were decreased by the 5-HT(1A) agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) in SERT +/+ and +/- mice. All drug-induced head twitches were blocked by the 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonist a-Phenyl-1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidinemethanol (MDL 11,939).
Conclusions and implications: These data show that indirect activation of 5-HT(2A) receptors via blockade of presynaptic 5-HT(1A) receptors potentiated head-twitch responses, suggesting functional interactions between these receptors, interactions affected by altered 5-HT availability. Our findings strongly support the correlation of WAY 100635 induced head twitches with increased 5-HT availability, induced genetically or pharmacologically.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The mechanism by which the selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist S-(-) UH 301 produces head-twitches in mice.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1996 Sep;55(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(96)00072-x. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1996. PMID: 8870031
-
The serotonin 5-HT(2A) receptor agonist TCB-2: a behavioral and neurophysiological analysis.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010 Sep;212(1):13-23. doi: 10.1007/s00213-009-1694-1. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010. PMID: 19823806
-
Chronic treatment with fluoxetine decreases cerebral metabolic responses to the 5-HT1A agonist 8-hydroxy-2(di-N-propylamino)tetralin and increases those to the 5-HT2A/2C agonist 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane and to the dopaminergic agonist apomorphine.Brain Res. 2010 Jun 4;1335:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.090. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20381465
-
A pharmacological analysis of mice with a targeted disruption of the serotonin transporter.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007 Dec;195(2):147-66. doi: 10.1007/s00213-007-0910-0. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17712549 Review.
-
Effects of the antidepressant fluoxetine on the subcellular localization of 5-HT1A receptors and SERT.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Sep 5;367(1601):2416-25. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0361. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22826342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardamonin Modulates Neuropathic Pain through the Possible Involvement of Serotonergic 5-HT1A Receptor Pathway in CCI-Induced Neuropathic Pain Mice Model.Molecules. 2021 Jun 16;26(12):3677. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123677. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34208700 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin mediation of early memory formation via 5-HT2B receptor-induced glycogenolysis in the day-old chick.Front Pharmacol. 2014 Apr 1;5:54. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00054. eCollection 2014. Front Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24744730 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Activity Relationships for Psilocybin, Baeocystin, Aeruginascin, and Related Analogues to Produce Pharmacological Effects in Mice.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Nov 2;5(11):1181-1196. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00177. eCollection 2022 Nov 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36407948 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the head-twitch response induced by hallucinogens in mice: detection of the behavior based on the dynamics of head movement.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Jun;227(4):727-39. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3006-z. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23407781 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hallucinogens on Unconditioned Behavior.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:159-199. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_466. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28224459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrews AM, Murphy DL. Sustained depletion of cortical and hippocampal serotonin and norepinephrine but not striatal dopamine by 1-methyl-4-(2′-aminophenyl)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (2′-NH2-MPTP): a comparative study with 2′-CH3-MPTP and MPTP. J Neurochem. 1993;60:1167–1170. - PubMed
-
- Bengel D, Murphy DL, Andrews AM, Wichems CH, Feltner D, Heils A, et al. Altered brain serotonin homeostasis and locomotor insensitivity to 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (‘Ecstasy’) in serotonin transporter-deficient mice. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;53:649–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

