Primary prevention from the epidemiology perspective: three examples from the practice
- PMID: 20128907
- PMCID: PMC2829018
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-10-10
Primary prevention from the epidemiology perspective: three examples from the practice
Abstract
Background: Primary prevention programmes are of increasing importance to reduce the impact of chronic diseases on the individual, institutional and societal level. However, most initiatives that develop and implement primary prevention programmes are not evaluated with scientific rigor. On the basis of three different projects we discuss necessary steps on the road to evidence-based primary prevention.
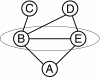
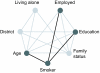
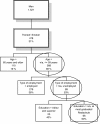
Discussion: We first discuss how to identify suitable target groups exploiting sophisticated statistical methods. This is illustrated using data from a health survey conducted in a federal state of Germany. A literature review is the more typical approach to identify target groups that is demonstrated using a European project on the prevention of childhood obesity. In the next step, modifiable risk factors and realistic targets of the intervention have to be specified. These determine the outcome measures that in turn are used for effect evaluation. Both, the target groups and the outcome measures, lay the ground for the study design and the definition of comparison groups as can be seen in our European project. This project also illustrates the development and implementation of a prevention programme. These may require active involvement of participants which can be achieved by participatory approaches taking into account the socio-cultural and living environment. Evaluation is of utmost importance for any intervention to assess structure, process and outcome according to rigid scientific criteria. Different approaches used for this are discussed and illustrated by a methodological project developed within a health promotion programme in a deprived area. Eventually the challenge of transferring an evidence-based intervention into practice and to achieve its sustainability is addressed.
Summary: This article describes a general roadmap to primary prevention comprising (1) the identification of target groups and settings, (2) the identification of modifiable risk factors and endpoints, (3) the development and implementation of an intervention programme, (4) the evaluation of structure, process and outcome and (5) the transfer of an evidence-based intervention into practice.
Figures
References
-
- Das Deutsche Cochrane Zentrum (oJ) Von der Evidenz zur Empfehlung. http://www.cochrane.de/de/gradesys.htm
-
- Jahn I, Foraita R, Pohlabeln H. Rauchen. Gewicht. Bewegung. Früherkennung. Zielgruppen für Prävention und Gesundheitsförderung im Land Bremen. Eine geschlechtervergleichende Auswertung der Bremer Umfrage GESUNDHEIT! Zweiter Ergebnisbericht einer Umfrage bei Bürgerinnen und Bürgern in Bremen und Bremerhaven. 2006. http://www.bips.uni-bremen.de/data/bericht_gesundheit_gesamt.pdf
-
- Summerbell CD, Ashton V, Campbell KJ, Edmunds L, Kelly S, Waters E. Interventions for treating obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. p. CD001872. - PubMed
-
- Summerbell CD, Waters E, Edmunds LD, Kelly S, Brown T, Campbell KJ. Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. p. CD001871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

