SLUG: a new target of lymphoid enhancer factor-1 in human osteoblasts
- PMID: 20128911
- PMCID: PMC2834684
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-13
SLUG: a new target of lymphoid enhancer factor-1 in human osteoblasts
Abstract
Background: Lymphoid Enhancer Factor-1 (Lef-1) is a member of a transcription factor family that acts as downstream mediator of the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway which plays a critical role in osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. In a search for Lef-1 responsive genes in human osteoblasts, we focused on the transcriptional regulation of the SLUG, a zinc finger transcription factor belonging to the Snail family of developmental proteins. Although the role of SLUG in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell motility during embryogenesis is well documented, the functions of this factor in most normal adult human tissues are largely unknown. In this study we investigated SLUG expression in normal human osteoblasts and their mesenchymal precursors, and its possible correlation with Lef-1 and Wnt/beta-catenin signalling.
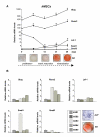
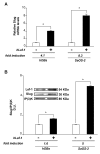
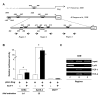
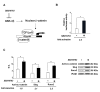
Results: The experiments were performed on normal human primary osteoblasts obtained from bone fragments, cultured in osteogenic conditions in presence of Lef-1 expression vector or GSK-3beta inhibitor, SB216763. We demonstrated that the transcription factor SLUG is present in osteoblasts as well as in their mesenchymal precursors obtained from Wharton's Jelly of human umbilical cord and induced to osteoblastic differentiation. We found that SLUG is positively correlated with RUNX2 expression and deposition of mineralized matrix, and is regulated by Lef-1 and beta-catenin. Consistently, Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay, used to detect the direct Lef/Tcf factors that are responsible for the promoter activity of SLUG gene, demonstrated that Lef-1, TCF-1 and TCF4 are recruited to the SLUG gene promoter "in vivo".
Conclusion: These studies provide, for the first time, the evidence that SLUG expression is correlated with osteogenic commitment, and is positively regulated by Lef-1 signal in normal human osteoblasts. These findings will help to further understand the regulation of the human SLUG gene and reveal the biological functions of SLUG in the context of bone tissue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The transcription factor LEF-1 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition in MDCK cells independent of β-catenin.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Dec 6;442(1-2):133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.11.031. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 24269234
-
Differentiation-inducing factor-1 alters canonical Wnt signaling and suppresses alkaline phosphatase expression in osteoblast-like cell lines.J Bone Miner Res. 2006 Aug;21(8):1307-16. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.060512. J Bone Miner Res. 2006. PMID: 16869729
-
FHL2 mediates dexamethasone-induced mesenchymal cell differentiation into osteoblasts by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling-dependent Runx2 expression.FASEB J. 2008 Nov;22(11):3813-22. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-106302. Epub 2008 Jul 24. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 18653765
-
Beta-catenin/LEF-1 signalling in breast cancer--central players activated by a plethora of inputs.Cells Tissues Organs. 2007;185(1-3):51-60. doi: 10.1159/000101303. Cells Tissues Organs. 2007. PMID: 17587808 Review.
-
Lymphoid enhancer factor/T cell factor expression in colorectal cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004 Jan-Jun;23(1-2):41-52. doi: 10.1023/a:1025858928620. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004. PMID: 15000148 Review.
Cited by
-
Repression of Wnt/β-catenin response elements by p63 (TP63).Cell Cycle. 2016;15(5):699-710. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1148837. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26890356 Free PMC article.
-
Low-level overexpression of p53 promotes warfarin-induced calcification of porcine aortic valve interstitial cells by activating Slug gene transcription.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 9;293(10):3780-3792. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.791145. Epub 2018 Jan 22. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29358327 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular regulation of Snai2 in development and disease.J Cell Sci. 2019 Dec 2;132(23):jcs235127. doi: 10.1242/jcs.235127. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31792043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Boolean modeling of mechanosensitive epithelial to mesenchymal transition and its reversal.iScience. 2023 Mar 2;26(4):106321. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106321. eCollection 2023 Apr 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36968076 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of breast cancer metastasis by Runx2 and estrogen signaling: the role of SNAI2.Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):R127. doi: 10.1186/bcr3073. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22151997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barker N. The canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;468:5–15. full_text. - PubMed
-
- Matsuzaki E, Takahashi-Yanaga F, Miwa Y, Hirata M, Watanabe Y, Sato N, Morimoto S, Hirofuji T, Maeda K, Sasaguri T. Differentiation-inducing factor-1 alters canonical Wnt signalling and suppresses alkaline phosphatase expression in osteoblast-like cell lines. J Bone Miner Res. 2006;21(8):1307–16. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.060512. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

