An evolved ribosome-inactivating protein targets and kills human melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 20128926
- PMCID: PMC2828990
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-28
An evolved ribosome-inactivating protein targets and kills human melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Background: Few treatment options exist for patients with metastatic melanoma, resulting in poor prognosis. One standard treatment, dacarbazine (DTIC), shows low response rates ranging from 15 to 25 percent with an 8-month median survival time. The development of targeted therapeutics with novel mechanisms of action may improve patient outcome. Ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) such as Shiga-like Toxin 1 (SLT-1) represent powerful scaffolds for developing selective anticancer agents. Here we report the discovery and properties of a single chain ribosome-inactivating protein (scRIP) derived from the cytotoxic A subunit of SLT-1 (SLT-1A), harboring the 7-amino acid peptide insertion IYSNKLM (termed SLT-1A IYSNKLM) allowing the toxin variant to selectively target and kill human melanoma cells.
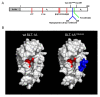
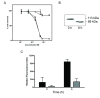
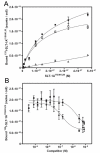
Results: SLT-1A IYSNKLM was able to kill 7 of 8 human melanoma cell lines. This scRIP binds to 518-A2 human melanoma cells with a dissociation constant of 18 nM, resulting in the blockage of protein synthesis and apoptosis in such cells. Biodistribution and imaging studies of radiolabeled SLT-1A IYSNKLM administered intravenously into SCID mice bearing a human melanoma xenograft indicate that SLT-1AI YSNKLM readily accumulates at the tumor site as opposed to non-target tissues. Furthermore, the co-administration of SLT-1A IYSNKLM with DTIC resulted in tumor regression and greatly increased survival in this mouse xenograft model in comparison to DTIC or SLT-1A IYSNKLM treatment alone (115 day median survival versus 46 and 47 days respectively; P values < 0.001). SLT-1A IYSNKLM is stable in serum and its intravenous administration resulted in modest immune responses following repeated injections in CD1 mice.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that the evolution of a scRIP template can lead to the discovery of novel cancer cell-targeted compounds and in the case of SLT-1A IYSNKLM can specifically kill human melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Probing the surface of eukaryotic cells using combinatorial toxin libraries.Curr Biol. 2001 May 1;11(9):697-701. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00207-x. Curr Biol. 2001. PMID: 11369233
-
SLT-VEGF reduces lung metastases, decreases tumor recurrence, and improves survival in an orthotopic melanoma model.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Sep;2(9):2242-57. doi: 10.3390/toxins2092242. Epub 2010 Aug 27. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069683 Free PMC article.
-
Charged and hydrophobic surfaces on the a chain of shiga-like toxin 1 recognize the C-terminal domain of ribosomal stalk proteins.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031191. Epub 2012 Feb 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22355345 Free PMC article.
-
The use of Shiga-like toxin 1 in cancer therapy.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2001 Jul-Aug;39(1-2):99-106. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(01)00126-3. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2001. PMID: 11418306 Review.
-
Escherichia coli cytotoxins and enterotoxins.Can J Microbiol. 1992 Jul;38(7):734-46. doi: 10.1139/m92-120. Can J Microbiol. 1992. PMID: 1393838 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of ribosome-inactivating proteins from Sambucus for the construction of immunotoxins and conjugates for cancer therapy.Toxins (Basel). 2011 May;3(5):420-41. doi: 10.3390/toxins3050420. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotoxins: a promising treatment modality for metastatic melanoma?Ochsner J. 2010 Fall;10(3):193-9. Ochsner J. 2010. PMID: 21603377 Free PMC article.
-
Translation regulation in skin cancer from a tRNA point of view.Epigenomics. 2019 Feb;11(2):215-245. doi: 10.2217/epi-2018-0176. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Epigenomics. 2019. PMID: 30565492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in the ribosomal machinery in cancer and hematologic disorders.J Hematol Oncol. 2012 Jun 18;5:32. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-5-32. J Hematol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22709827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of ricin and Shiga toxins with ribosomes.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;357:1-18. doi: 10.1007/82_2011_174. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21910078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

