HBO1 histone acetylase activity is essential for DNA replication licensing and inhibited by Geminin
- PMID: 20129055
- PMCID: PMC2818871
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.012
HBO1 histone acetylase activity is essential for DNA replication licensing and inhibited by Geminin
Abstract
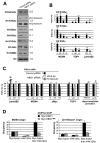
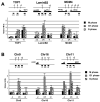
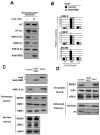
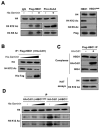
HBO1, an H4-specific histone acetylase, is a coactivator of the DNA replication licensing factor Cdt1. HBO1 acetylase activity is required for licensing, because a histone acetylase (HAT)-defective mutant of HBO1 bound at origins is unable to load the MCM complex. H4 acetylation at origins is cell-cycle regulated, with maximal activity at the G1/S transition, and coexpression of HBO1 and Jade-1 increases histone acetylation and MCM complex loading. Overexpression of the Set8 histone H4 tail-binding domain specifically inhibits MCM loading, suggesting that histones are a physiologically relevant target for licensing. Lastly, Geminin inhibits HBO1 acetylase activity in the context of a Cdt1-HBO1 complex, and it associates with origins and inhibits H4 acetylation and licensing in vivo. Thus, H4 acetylation at origins by HBO1 is critical for replication licensing by Cdt1, and negative regulation of licensing by Geminin is likely to involve inhibition of HBO1 histone acetylase activity.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Histone acetylation by HBO1 tightens replication licensing.Mol Cell. 2010 Jan 15;37(1):5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.028. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20129050 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Chromatin unfolding by Cdt1 regulates MCM loading via opposing functions of HBO1 and HDAC11-geminin.Cell Cycle. 2010 Nov 1;9(21):4351-63. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.21.13596. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20980834 Free PMC article.
-
HBO1 histone acetylase is a coactivator of the replication licensing factor Cdt1.Genes Dev. 2008 Oct 1;22(19):2633-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.1674108. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18832067 Free PMC article.
-
JNK1 phosphorylation of Cdt1 inhibits recruitment of HBO1 histone acetylase and blocks replication licensing in response to stress.Mol Cell. 2011 Oct 7;44(1):62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.06.021. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21856198 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering structure, function and mechanism of lysine acetyltransferase HBO1 in protein acetylation, transcription regulation, DNA replication and its oncogenic properties in cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Feb;77(4):637-649. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03296-x. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31535175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cdt1 and geminin in DNA replication initiation.Subcell Biochem. 2012;62:71-87. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4572-8_5. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22918581 Review.
Cited by
-
Flipping the switch from g1 to s phase with e3 ubiquitin ligases.Genes Cancer. 2012 Nov;3(11-12):634-48. doi: 10.1177/1947601912473307. Genes Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23634252 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase D1 phosphorylation of KAT7 enhances its protein stability and promotes replication licensing and cell proliferation.Cell Death Discov. 2020 Sep 18;6(1):89. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-00323-w. eCollection 2020. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 33014433 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic control of cofilin and αTAT in living cells using Z-lock.Nat Chem Biol. 2019 Dec;15(12):1183-1190. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0405-4. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Nat Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31740825 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of model replication origins in Drosophila reveals new aspects of the chromatin landscape and its relationship to origin activity and the prereplicative complex.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jan;23(1):200-12. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-05-0409. Epub 2011 Nov 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22049023 Free PMC article.
-
MMSET is dynamically regulated during cell-cycle progression and promotes normal DNA replication.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(1):95-105. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1121323. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26771714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal BD, Calvi BR. Chromatin regulates origin activity in Drosophila follicle cells. Nature. 2004;430:372–376. - PubMed
-
- Arias EE, Walter JC. Strength in numbers: preventing rereplication via multiple mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. Genes Dev. 2007;21:497–518. - PubMed
-
- Bell SP, Dutta A. DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:333–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

