IAP regulation of metastasis
- PMID: 20129247
- PMCID: PMC2818597
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.11.021
IAP regulation of metastasis
Abstract
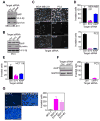
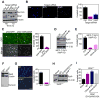
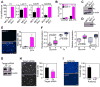
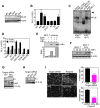
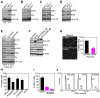
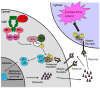
Inhibitor-of-Apoptosis (IAP) proteins contribute to tumor progression, but the requirements of this pathway are not understood. Here, we show that intermolecular cooperation between XIAP and survivin stimulates tumor cell invasion and promotes metastasis. This pathway is independent of IAP inhibition of cell death. Instead, a survivin-XIAP complex activates NF-kappaB, which in turn leads to increased fibronectin gene expression, signaling by beta1 integrins, and activation of cell motility kinases FAK and Src. Therefore, IAPs are direct metastasis genes, and their antagonists could provide antimetastatic therapies in patients with cancer.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Altieri DC. Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:61–70. - PubMed
-
- Birkey Reffey S, Wurthner JU, Parks WT, Roberts AB, Duckett CS. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein functions as a cofactor in transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:26542–26549. - PubMed
-
- Bittner M, Meltzer P, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Seftor E, Hendrix M, Radmacher M, Simon R, Yakhini Z, Ben-Dor A, et al. Molecular classification of cutaneous malignant melanoma by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;406:536–540. - PubMed
-
- Bouchard V, Harnois C, Demers MJ, Thibodeau S, Laquerre V, Gauthier R, Vezina A, Noel D, Fujita N, Tsuruo T, et al. B1 integrin/Fak/Src signaling in intestinal epithelial crypt cell survival: integration of complex regulatory mechanisms. Apoptosis. 2008;13:531–542. - PubMed
-
- Bredesen DE, Mehlen P, Rabizadeh S. Receptors that mediate cellular dependence. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:1031–1043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA078810/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA089720/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA118005/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA78810/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL054131/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA109874/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA90917/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA107548/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA107548/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54131/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL054131/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA89720/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 CA089720/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA118005/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA090917/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

