A novel antisense RNA regulates at transcriptional level the virulence gene icsA of Shigella flexneri
- PMID: 20129941
- PMCID: PMC2879508
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq025
A novel antisense RNA regulates at transcriptional level the virulence gene icsA of Shigella flexneri
Abstract
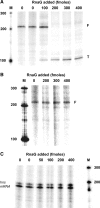
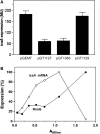
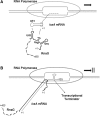
The virulence gene icsA of Shigella flexneri encodes an invasion protein crucial for host colonization by pathogenic bacteria. Within the intergenic region virA-icsA, we have discovered a new gene that encodes a non-translated antisense RNA (named RnaG), transcribed in cis on the complementary strand of icsA. In vitro transcription assays show that RnaG promotes premature termination of transcription of icsA mRNA. Transcriptional inhibition is also observed in vivo by monitoring the expression profile in Shigella by real-time polymerase chain reaction and when RnaG is provided in trans. Chemical and enzymatic probing of the leader region of icsA mRNA either free or bound to RnaG indicate that upon hetero-duplex formation an intrinsic terminator, leading to transcription block, is generated on the nascent icsA mRNA. Mutations in the hairpin structure of the proposed terminator impair the RnaG mediated-regulation of icsA transcription. This study represents the first evidence of transcriptional attenuation mechanism caused by a small RNA in Gram-negative bacteria. We also present data on the secondary structure of the antisense region of RnaG. In addition, alternatively silencing icsA and RnaG promoters, we find that transcription from the strong RnaG promoter reduces the activity of the weak convergent icsA promoter through the transcriptional interference regulation.
Figures



References
-
- Altuvia S. Identification of bacterial small non-coding RNAs: experimental approaches. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007;10:257–261. - PubMed
-
- Gottesman S. The small RNA regulators of Escherichia coli: roles and mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004;58:303–328. - PubMed
-
- Gottesman S. Stealth regulation: biological circuits with small RNA switches. Genes Dev. 2002;16:2829–2842. - PubMed
-
- Storz G, Opdyke JA, Zhang A. Controlling mRNA stability and translation with small, noncoding RNAs. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004;7:140–144. - PubMed

