InhA1, NprA, and HlyII as candidates for markers to differentiate pathogenic from nonpathogenic Bacillus cereus strains
- PMID: 20129969
- PMCID: PMC2849619
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02123-09
InhA1, NprA, and HlyII as candidates for markers to differentiate pathogenic from nonpathogenic Bacillus cereus strains
Abstract
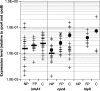
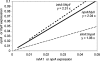
Bacillus cereus is found in food, soil, and plants, and the ability to cause food-borne diseases and opportunistic infection presumably varies among strains. Therefore, measuring harmful toxin production, in addition to the detection of the bacterium itself, may be key for food and hospital safety purposes. All previous studies have focused on the main known virulence factors, cereulide, Hbl, Nhe, and CytK. We examined whether other virulence factors may be specific to pathogenic strains. InhA1, NprA, and HlyII have been described as possibly contributing to B. cereus pathogenicity. We report the prevalence and expression profiles of these three new virulence factor genes among 57 B. cereus strains isolated from various sources, including isolates associated with gastrointestinal and nongastrointestinal diseases. Using PCR, quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR, and virulence in vivo assays, we unraveled these factors as potential markers to differentiate pathogenic from nonpathogenic strains. We show that the hlyII gene is carried only by strains with a pathogenic potential and that the expression levels of inhA1 and nprA are higher in the pathogenic than in the nonpathogenic group of strains studied. These data deliver useful information about the pathogenicity of various B. cereus strains.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson Borge, G. I., M. Skeie, T. Sorhaug, T. Langsrud, and P. E. Granum. 2001. Growth and toxin profiles of Bacillus cereus isolated from different food sources. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 69:237-246. - PubMed
-
- Andreeva, Z., V. Nesterenko, M. Fomkina, V. Ternosky, N. Suzina, A. Bakulina, A. Solonin, and E. Sineva. 2007. The properties of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II pores depend on environmental conditions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1768:253-263. - PubMed
-
- Andreeva, Z., V. Nesterenko, I. Yurkov, Z. I. Budarina, E. Sineva, and A. S. Solonin. 2006. Purification and cytotoxic properties of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II. Protein Expr. Purif. 47:186-193. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 2009. The community summary report on food-borne outbreaks in the European Union in 2007. The EFSA J. 2009(May):271.
-
- Arnaout, M., R. Tamburro, S. Bodner, J. Sandlund, G. Rivera, and C. Pui. 1999. Bacillus cereus causing fulminant sepsis and hemolysis in two patients with acute leukemia. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 21:431-435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

