SNVMix: predicting single nucleotide variants from next-generation sequencing of tumors
- PMID: 20130035
- PMCID: PMC2832826
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq040
SNVMix: predicting single nucleotide variants from next-generation sequencing of tumors
Abstract
Motivation: Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has enabled whole genome and transcriptome single nucleotide variant (SNV) discovery in cancer. NGS produces millions of short sequence reads that, once aligned to a reference genome sequence, can be interpreted for the presence of SNVs. Although tools exist for SNV discovery from NGS data, none are specifically suited to work with data from tumors, where altered ploidy and tumor cellularity impact the statistical expectations of SNV discovery.
Results: We developed three implementations of a probabilistic Binomial mixture model, called SNVMix, designed to infer SNVs from NGS data from tumors to address this problem. The first models allelic counts as observations and infers SNVs and model parameters using an expectation maximization (EM) algorithm and is therefore capable of adjusting to deviation of allelic frequencies inherent in genomically unstable tumor genomes. The second models nucleotide and mapping qualities of the reads by probabilistically weighting the contribution of a read/nucleotide to the inference of a SNV based on the confidence we have in the base call and the read alignment. The third combines filtering out low-quality data in addition to probabilistic weighting of the qualities. We quantitatively evaluated these approaches on 16 ovarian cancer RNASeq datasets with matched genotyping arrays and a human breast cancer genome sequenced to >40x (haploid) coverage with ground truth data and show systematically that the SNVMix models outperform competing approaches.
Availability: Software and data are available at http://compbio.bccrc.ca
Contact: sshah@bccrc.ca SUPPLEMANTARY INFORMATION: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures

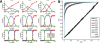
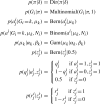
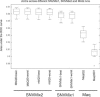
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

