Indole-3-carbinol triggers aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent estrogen receptor (ER)alpha protein degradation in breast cancer cells disrupting an ERalpha-GATA3 transcriptional cross-regulatory loop
- PMID: 20130088
- PMCID: PMC2847521
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-08-0689
Indole-3-carbinol triggers aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent estrogen receptor (ER)alpha protein degradation in breast cancer cells disrupting an ERalpha-GATA3 transcriptional cross-regulatory loop
Abstract
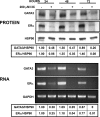
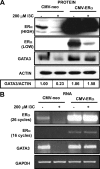
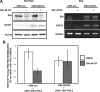
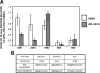
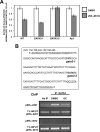
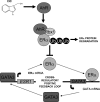
Estrogen receptor (ER)alpha is a critical target of therapeutic strategies to control the proliferation of hormone-dependent breast cancers. Preferred clinical options have significant adverse side effects that can lead to treatment resistance due to the persistence of active estrogen receptors. We have established the cellular mechanism by which indole-3-carbinol (I3C), a promising anticancer phytochemical from Brassica vegetables, ablates ERalpha expression, and we have uncovered a critical role for the GATA3 transcription factor in this indole-regulated cascade. I3C-dependent activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) initiates Rbx-1 E3 ligase-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of ERalpha protein. I3C inhibits endogenous binding of ERalpha with the 3'-enhancer region of GATA3 and disrupts endogenous GATA3 interactions with the ERalpha promoter, leading to a loss of GATA3 and ERalpha expression. Ectopic expression of GATA3 has no effect on I3C-induced ERalpha protein degradation but does prevent I3C inhibition of ERalpha promoter activity, demonstrating the importance of GATA3 in this I3C-triggered cascade. Our preclinical results implicate I3C as a novel anticancer agent in human cancers that coexpress ERalpha, GATA3, and AhR, a combination found in a large percentage of breast cancers but not in other critical ERalpha target tissues essential to patient health.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Indole-3-carbinol and its N-alkoxy derivatives preferentially target ERα-positive breast cancer cells.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(16):2587-99. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2015.942210. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486199 Free PMC article.
-
Indole-3-carbinol downregulation of telomerase gene expression requires the inhibition of estrogen receptor-alpha and Sp1 transcription factor interactions within the hTERT promoter and mediates the G1 cell cycle arrest of human breast cancer cells.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Sep;32(9):1315-23. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr116. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21693539 Free PMC article.
-
Indole-3-carbinol disrupts estrogen receptor-alpha dependent expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and insulin receptor substrate-1 and proliferation of human breast cancer cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Nov 5;363(1-2):74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.07.008. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22835548 Free PMC article.
-
Indole-3-carbinol induces tumor cell death: function follows form.J Surg Res. 2016 Jul;204(1):47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.04.021. Epub 2016 Apr 22. J Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27451867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular targets and anticancer potential of indole-3-carbinol and its derivatives.Cell Cycle. 2005 Sep;4(9):1201-15. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.9.1993. Epub 2005 Sep 6. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 16082211 Review.
Cited by
-
Artemisinin triggers a G1 cell cycle arrest of human Ishikawa endometrial cancer cells and inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase-4 promoter activity and expression by disrupting nuclear factor-κB transcriptional signaling.Anticancer Drugs. 2014 Mar;25(3):270-81. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000054. Anticancer Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24296733 Free PMC article.
-
1-Benzyl-indole-3-carbinol is a highly potent new small molecule inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in melanoma cells that coordinately inhibits cell proliferation and disrupts expression of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor isoform-M.Carcinogenesis. 2017 Dec 7;38(12):1207-1217. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgx103. Carcinogenesis. 2017. PMID: 29028954 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Therapy to Modulate Tryptophan Metabolism and Aryl Hydrocarbon-Receptor Signaling Activation in Human Diseases.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 17;12(9):2846. doi: 10.3390/nu12092846. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32957545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genus Eriosema (Fabaceae): From the Ethnopharmacology to an Evidence-Based Phytotherapeutic Perspective?Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 7;12:641225. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.641225. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34025412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Its Crosstalk: A Chemopreventive Target of Naturally Occurring and Modified Phytochemicals.Molecules. 2024 Sep 10;29(18):4283. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184283. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afouda B. A., Martin J., Liu F., Ciau-Uitz A., Patient R., Hoppler S. GATA transcription factors integrate Wnt signalling during heart development. Development. 2008;135:3185–3190. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal B. B., Ichikawa H. Molecular targets and anticancer potential of indole-3-carbinol and its derivatives. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:1201–1215. - PubMed
-
- Ali S., Coombes R. C. Estrogen receptor alpha in human breast cancer: occurrence and significance. J Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia. 2000;5:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Antkiewicz D. S., Burns C. G., Carney S. A., Peterson R. E., Heideman W. Heart malformation is an early response to TCDD in embryonic zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. 2005;84:368–377. - PubMed
-
- Asselin-Labat M. L. Mammary stem and progenitor cells: critical role of the transcription factor Gata-3. Med. Sci. 2007;23:1077–1080. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

