12-Lipoxygenase regulates hippocampal long-term potentiation by modulating L-type Ca2+ channels
- PMID: 20130191
- PMCID: PMC2835505
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2168-09.2010
12-Lipoxygenase regulates hippocampal long-term potentiation by modulating L-type Ca2+ channels
Abstract
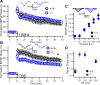
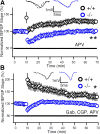
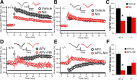
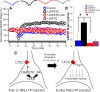
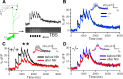
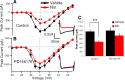
Although long-term potentiation (LTP) has been intensively studied, there is disagreement as to which molecules mediate and modulate LTP. This is partly attributable to the presence of mechanistically distinct forms of LTP that are induced by different patterns of stimulation and that depend on distinct Ca(2+) sources. Here, we report a novel role for the arachidonic acid-metabolizing enzyme 12-lipoxygenase (12-LO) in LTP at CA3-CA1 hippocampal synapses that is dependent on the pattern of tetanic stimulation. We find that 12-LO activity is required for the induction of LTP in response to a theta burst stimulation protocol that depends on Ca(2+) influx through both NMDA receptors and L-type voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels. In contrast, LTP induced by 100 Hz tetanic stimulation, which requires Ca(2+) influx through NMDA receptors but not L-type channels, does not require 12-LO. We find that 12-LO regulates LTP by enhancing postsynaptic somatodendritic Ca(2+) influx through L-type channels during theta burst stimulation, an action exerted via 12(S)-HPETE [12(S)-hydroperoxyeicosa-5Z,8Z,10E,14Z-tetraenoic acid], a downstream metabolite of 12-LO. These results help define the role of a long-disputed signaling enzyme in LTP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
12-lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid mediate metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression at hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses.J Neurosci. 2003 Dec 10;23(36):11427-35. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-36-11427.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14673007 Free PMC article.
-
Steroid pregnenolone sulfate enhances NMDA-receptor-independent long-term potentiation at hippocampal CA1 synapses: role for L-type calcium channels and sigma-receptors.Hippocampus. 2007;17(5):349-69. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20273. Hippocampus. 2007. PMID: 17330865
-
Mechanisms of NMDA Receptor- and Voltage-Gated L-Type Calcium Channel-Dependent Hippocampal LTP Critically Rely on Proteolysis That Is Mediated by Distinct Metalloproteinases.J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 1;37(5):1240-1256. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2170-16.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28069922 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and signal amplification of NMDA receptors.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):71-84. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.80. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725510 Review.
-
Neurophysiological analysis of long-term potentiation in mammalian brain.Behav Brain Res. 1995 Jan 23;66(1-2):45-52. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(94)00123-w. Behav Brain Res. 1995. PMID: 7755898 Review.
Cited by
-
Nitric Oxide Is Required for L-Type Ca(2+) Channel-Dependent Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2016 Jun 29;8:17. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2016.00017. eCollection 2016. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27445786 Free PMC article.
-
High extracellular Ca2+ stimulates Ca2+-activated Cl- currents in frog parathyroid cells through the mediation of arachidonic acid cascade.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 29;6(4):e19158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019158. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21559478 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative-stress induced increase in circulating fatty acids does not contribute to phospholipase A2-dependent appetitive long-term memory failure in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis.BMC Neurosci. 2014 May 1;15:56. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-15-56. BMC Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24886155 Free PMC article.
-
Actions and Mechanisms of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Voltage-Gated Ion Channels.Front Physiol. 2017 Feb 6;8:43. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00043. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28220076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional biology of arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase-1 (ALOX15).Gene. 2015 Nov 15;573(1):1-32. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.07.073. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Gene. 2015. PMID: 26216303 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Besana A, Robinson RB, Feinmark SJ. Lipids and two-pore domain K+ channels in excitable cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005;77:103–110. - PubMed
-
- Buttner N, Siegelbaum SA, Volterra A. Direct modulation of Aplysia S-K+ channels by a 12-lipoxygenase metabolite of arachidonic acid. Nature. 1989;342:553–555. - PubMed
-
- Carlson G, Wang Y, Alger BE. Endocannabinoids facilitate the induction of LTP in the hippocampus. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:723–724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
