Desiccating stress promotion of Th17 differentiation by ocular surface tissues through a dendritic cell-mediated pathway
- PMID: 20130281
- PMCID: PMC2891467
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.09-3838
Desiccating stress promotion of Th17 differentiation by ocular surface tissues through a dendritic cell-mediated pathway
Abstract
Purpose: To explore the phenomenon that corneal and conjunctival tissues subjected to desiccating stress (DS) promote Th17 differentiation by stimulating the production of Th17-inducing cytokines through a dendritic cell (DC)-mediated pathway.
Methods: Experimental dry eye was created by subjecting C57BL/6 mice to desiccating environmental stress. Corneal and conjunctival explants from dry eye or control mice were cocultured with DCs for 24 hours before CD4(+) T cells were added for an additional 4 to 7 days. Expression of Th17-associated genes in the cornea, conjunctiva, DCs, and CD4(+) T cells was evaluated by real-time PCR. Cytokine concentrations in coculture supernatants were measured by immunobead assay. IL-17-producing T cells were identified by ELISPOT bioassay.
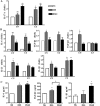
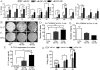
Results: Higher levels of IL-17A, TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, IL-6, IL-23, and IL-1beta mRNA transcripts and TGF-beta1, IL-6, and IL-1beta protein were observed in corneal epithelium and conjunctiva from dry eye mice. DCs cocultured with epithelial explants from dry eye mice for 2 days produced higher levels of TGF-beta1, IL-6, IL-23, and IL-1beta mRNA transcripts and of TGF-beta1, IL-6, and IL-1beta protein. CD4(+) T cells cocultured with DCs and epithelial explants from dry eye mice expressed increased levels of IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22, CCL-20, and retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor-gammat mRNA transcripts and increased IL-17A protein and number of IL-17-producing T cells (Th17 cells).
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that DS creates an environment on the ocular surface that stimulates the production of Th17-inducing cytokines by corneal and conjunctival epithelia that promote Th17 differentiation through a dendritic cell-mediated pathway.
Figures

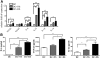

References
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol 1989;7:145–173 - PubMed
-
- McKenzie BS, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ. Understanding the IL-23-IL-17 immune pathway. Trends Immunol 2006;27:17–23 - PubMed
-
- Steinman L. A brief history of T(H)17, the first major revision in the T(H)1/T(H)2 hypothesis of T cell-mediated tissue damage. Nat Med 2007;13:139–145 - PubMed
-
- Komiyama Y, Nakae S, Matsuki T, et al. IL-17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 2006;177:566–573 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

