Neural compensation for long-term asymmetric optical blur to improve visual performance in keratoconic eyes
- PMID: 20130284
- PMCID: PMC2904023
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.09-4558
Neural compensation for long-term asymmetric optical blur to improve visual performance in keratoconic eyes
Abstract
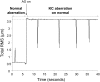
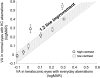
Purpose. To investigate whether long-term visual experience with irregular optical blur compensates for the impact of higher-order aberration on visual performance in keratoconic (KC) eyes. Methods. The aberrations and high (100%)- and low (20%)-contrast tumbling E visual acuity (VA) were measured in four moderate KC eyes in which the subjects were wearing their own prescribed soft toric contact lenses over a 6-mm pupil. VA was measured in three emmetropic normal eyes for comparison with each of the four KC eyes. An adaptive optics system was used to correct the aberration of the normal eye and to induce the aberration of the KC eye simultaneously during vision testing. The magnitude of neural compensation was defined as improvement in VA in each KC eye compared with the normal eyes with KC aberrations. Results. Mean total and higher-order root mean square errors in the KC eyes with contact lenses were 2.72 +/- 0.83 mum and 1.36 +/- 0.29 mum, respectively, for a 6-mm pupil. Residual RMS wavefront error in induction of KC aberrations on normal eyes was approximately 0.1 mum in all cases. Each KC eye had statistically better high (P < 0.02)- and low (P < 0.03)-contrast VA than the three normal eyes. Mean compensation for high-contrast VA in logMAR was 0.12 +/- 0.09, corresponding to an improvement of 23.8%. A similar result was obtained for low-contrast VA. The magnitude of compensation increased with the severity of KC aberrations. Conclusions. In KC eyes, the neural visual system compensates for long-term visual experience with an asymmetrically blurred retinal image, resulting in improved visual performance.
Figures


References
-
- Smirnov MS. Measurement of the wave aberration of the human eye. Biophysics 1962;7:766–795 - PubMed
-
- Porter J, Guirao A, Cox IG, Williams DR. Monochromatic aberrations of the human eye in a large population. J Opt Soc Am A 2001;18:1793–1803 - PubMed
-
- Thibos L, Hong X, Bradley A, Cheng X. Statistical variation of aberration structure and image quality in a normal population of healthy eyes. J Opt Soc Am A 2002;19:2329–2348 - PubMed
-
- Liang J, Williams DR. Aberrations and retinal image quality of the normal human eye. J Opt Soc Am A 1997;14:2873–2883 - PubMed
-
- Maeda N, Fujikado T, Kuroda T, et al. Wavefront aberrations measured with Hartmann-Shack sensor in patients with keratoconus. Ophthalmology 2002;109:1996–2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

