Lovastatin decreases acute mucosal inflammation via 15-epi-lipoxin A4
- PMID: 20130564
- PMCID: PMC3260795
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2009.141
Lovastatin decreases acute mucosal inflammation via 15-epi-lipoxin A4
Abstract
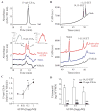
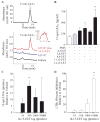
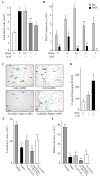
The widespread use of statins for hypercholesterolemia has uncovered pleiotropic anti-inflammatory properties that were unexpected based on the drugs' original design; yet, mechanisms for these protective actions remain uncertain. In this study lovastatin triggered biosynthesis of the anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediator 15-epi-lipoxin A(4) (15-epi-LXA(4)). During interactions between human neutrophils and airway epithelial cells, the statin-induced increase in 15-epi-LXA(4) was associated with increased 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (14,15-EET) generation. When added to activated neutrophils, 14,15-EET enhanced 15-epi-LXA(4) biosynthesis. In a murine model of airway mucosal injury and inflammation, lovastatin increased 15-epi-LXA(4) formation in vivo and markedly decreased acute lung inflammation. Administration of 15-epi-LXA(4) also inhibited lung inflammation in an additive manner with lovastatin. Together, these results indicate that statin-triggered 15-epi-LXA(4) generation during human leukocyte-airway epithelial cell interactions is an endogenous mechanism for statin-mediated tissue protection at mucosal surfaces that may also be relevant in the statins' ability to stimulate the resolution of inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES: CNS and BDL are co-inventors on patents on lipoxins that are assigned to Brigham and Women’s Hospital and have been licensed for clinical development and are the source of consultancies for BDL. The remaining authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Jain MK, Ridker PM. Anti-inflammatory effects of statins: clinical evidence and basic mechanisms. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2005;4(12):977–87. - PubMed
-
- Kwak B, Mulhaupt F, Myit S, Mach F. Statins as a newly recognized type of immunomodulator. Nature Medicine. 2000;6(12):1399–402. - PubMed
-
- Mira E, et al. Statins induce regulatory T cell recruitment via a CCL1 dependent pathway. J Immunol. 2008;181(5):11. - PubMed
-
- Murphy DM, et al. Simvastatin attenuates release of neutrophilic and remodeling factors from primary bronchial epithelial cells derived from stable lung transplant recipients. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Mar;294(3):L592–9. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi S, et al. Reversal of elastase-induced pulmonary emphysema and promotion of alveolar epithelial cell proliferation by simvastatin in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 May;294(5):L882–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

