Statistical analysis of variation in the human plasma proteome
- PMID: 20130815
- PMCID: PMC2814230
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/258494
Statistical analysis of variation in the human plasma proteome
Abstract
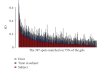
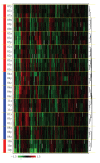
Quantifying the variation in the human plasma proteome is an essential prerequisite for disease-specific biomarker detection. We report here on the longitudinal and individual variation in human plasma characterized by two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis (2-D DIGE) using plasma samples from eleven healthy subjects collected three times over a two week period. Fixed-effects modeling was used to remove dye and gel variability. Mixed-effects modeling was then used to quantitate the sources of proteomic variation. The subject-to-subject variation represented the largest variance component, while the time-within-subject variation was comparable to the experimental variation found in a previous technical variability study where one human plasma sample was processed eight times in parallel and each was then analyzed by 2-D DIGE in triplicate. Here, 21 protein spots had larger than 50% CV, suggesting that these proteins may not be appropriate as biomarkers and should be carefully scrutinized in future studies. Seventy-eight protein spots showing differential protein levels between different individuals or individual collections were identified by mass spectrometry and further characterized using hierarchical clustering. The results present a first step toward understanding the complexity of longitudinal and individual variation in the human plasma proteome, and provide a baseline for improved biomarker discovery.
Figures




References
-
- Nedelkov D. Population proteomics: addressing protein diversity in humans. Expert Review of Proteomics. 2005;2(3):315–324. - PubMed
-
- Hermjakob H. The HUPO proteomics standards initiative—overcoming the fragmentation of proteomics data. Proteomics. 2006;1(S2):34–38. - PubMed
-
- Taylor CF. Minimum reporting requirements for proteomics: a MIAPE primer. Proteomics. 2006;1(S2):39–44. - PubMed
-
- Omenn GS. Exploring the human plasma proteome: editorial. Proteomics. 2005;5(13):3223–3225. - PubMed
-
- Omenn GS, Paik Y-K, Speicher D. The HUPO plasma proteome project: a report from the Munich congress. Proteomics. 2006;6(1):9–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

