A pilot study of maternal sensitivity in the context of emergent autism
- PMID: 20130975
- PMCID: PMC2904821
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-010-0948-4
A pilot study of maternal sensitivity in the context of emergent autism
Abstract
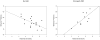
Unstructured mother-toddler interactions were examined in 18-month-old high- and low-risk children subsequently diagnosed (n = 12) or not diagnosed (n = 21) with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) at 36 months. Differences in maternal sensitivity were not found as a function of emergent ASD status. A differential-susceptibility moderation model of child risk guided investigations linking maternal sensitivity to child behavior and language growth. Group status moderated the relation between sensitivity and concurrent child behavior problems, with a positive association present for children with emergent ASD. Maternal sensitivity at 18 months predicted expressive language growth from age 2 to 3 years among children with emergent ASD only. Findings underscore the importance of understanding parent-child interaction during this key period in the development of autism symptomatology.
Figures
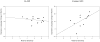
References
-
- Aber J, Belsky J, Slade A, Crnic K. Stability and change in mothers’ relationship representations with their toddlers. Developmental Psychology. 1999;35:1038–1047. - PubMed
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist 1 ½ - 5. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry; 2000.
-
- Aldred C, Green J, Adams C. A new social communication intervention for children with autism: pilot randomized controlled treatment study suggesting effectiveness. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 2004;45:1420–1430. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. American Psychiatric Association; Washington: 2000. Text Revision.
-
- Baker JK, Crnic KA. Thinking about feelings: Emotion focus in the parenting of Children with early developmental risk. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research. 2009;53:450–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

