The chlorosome: a prototype for efficient light harvesting in photosynthesis
- PMID: 20130996
- PMCID: PMC2882566
- DOI: 10.1007/s11120-010-9533-0
The chlorosome: a prototype for efficient light harvesting in photosynthesis
Abstract
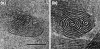
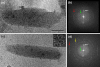
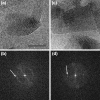
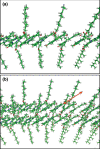
Three phyla of bacteria include phototrophs that contain unique antenna systems, chlorosomes, as the principal light-harvesting apparatus. Chlorosomes are the largest known supramolecular antenna systems and contain hundreds of thousands of BChl c/d/e molecules enclosed by a single membrane leaflet and a baseplate. The BChl pigments are organized via self-assembly and do not require proteins to provide a scaffold for efficient light harvesting. Their excitation energy flows via a small protein, CsmA embedded in the baseplate to the photosynthetic reaction centres. Chlorosomes allow for photosynthesis at very low light intensities by ultra-rapid transfer of excitations to reaction centres and enable organisms with chlorosomes to live at extraordinarily low light intensities under which no other phototrophic organisms can grow. This article reviews several aspects of chlorosomes: the supramolecular and molecular organizations and the light-harvesting and spectroscopic properties. In addition, it provides some novel information about the organization of the baseplate.
Figures



References
-
- Arellano JB, Melo TB, Borrego CM, Garcia-Gil J, Naqvi KR. Nanosecond laser photolysis studies of chlorosomes and artificial aggregates containing bacteriochlorophyll e: Evidence for the proximity of carotenoids and bacteriochlorophyll a in chlorosomes from Chlorobium phaeobacteroides strain CL1401. Photochem Photobiol. 2000;72:669–675. doi: 10.1562/0031-8655(2000)072<0669:NLPSOC>2.0.CO;2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balaban TS, Tamiaki H, Holzwarth AR. Chlorins programmed for self-assembly. Top Curr Chem. 2005;258:1–38. doi: 10.1007/b137480. - DOI
-
- Blankenship RE, Matsuura K (2003) Antenna complexes from green photosynthetic bacteria. In: Green BR, Parson WW (eds) Light-harvesting antennas in photosynthesis. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 195–217
-
- Blankenship RE, Olson JM, Miller M (1995) Antenna complexes from green photosynthetic bacteria. In: Blankenship RE, Madigan MT, Bauer CE (eds) Anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 399–435
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

