Pak1 and Pak2 are activated in recurrent respiratory papillomas, contributing to one pathway of Rac1-mediated COX-2 expression
- PMID: 20131316
- PMCID: PMC2932774
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.25226
Pak1 and Pak2 are activated in recurrent respiratory papillomas, contributing to one pathway of Rac1-mediated COX-2 expression
Abstract
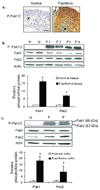
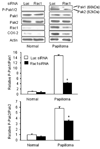
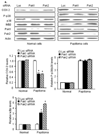
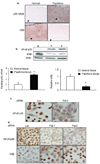
Recurrent respiratory papillomas are premalignant tumors of the airway caused by human papillomaviruses (HPVs), primarily Types 6 and 11. We had reported that respiratory papillomas overexpress the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), the small GTPase Rac1 and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and have enhanced nuclear factor-kappaB (NFkappaB) activation with decreased levels of IkappaB-beta but not IkappaB-alpha. We also showed that EGFR-activated Rac1 mediates expression of COX-2 through activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. We have now asked whether the p21-activated kinases Pak1 or Pak2 mediate activation of p38 by Rac1 in papilloma cells. Pak1 and Pak2 were constitutively activated in vivo in papilloma tissue compared with normal epithelium, and Rac1 siRNA reduced the level of both phospho-Pak1 and phospho-Pak2 in cultured papilloma cells. Reduction in Pak1 and Pak2 with siRNA decreased the COX-2 expression in papilloma cells, increased the levels of IkappaB-beta and reduced the nuclear localization of NF-kappaB, but had no effect on p38 phosphorylation. Our studies suggest that Rac1 --> Pak1/Pak2 --> NFkappaB is a separate pathway that contributes to the expression of COX-2 in HPV-induced papillomas, independently of the previously described Rac1 --> p38 --> COX-2 pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of Rac1 by epidermal growth factor mediates COX-2 expression in recurrent respiratory papillomas.Mol Med. 2007 Mar-Apr;13(3-4):143-50. doi: 10.2119/2007–00005.Wu. Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17592548 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression is mediated through phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, not mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase, in recurrent respiratory papillomas.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Sep 1;11(17):6155-61. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2664. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16144915
-
Activation of the small GTPase Rac1 by cGMP-dependent protein kinase.Cell Signal. 2004 Sep;16(9):1061-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.03.002. Cell Signal. 2004. PMID: 15212766
-
NF-kappaB- and C/EBPbeta-driven interleukin-1beta gene expression and PAK1-mediated caspase-1 activation play essential roles in interleukin-1beta release from Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4279-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412820200. Epub 2004 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15561713
-
Activation of endothelial ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) improves post-stroke recovery and angiogenesis via activating Pak1 in mice.Exp Neurol. 2019 Dec;322:113059. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113059. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31499064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional regulation of fibronectin by p21-activated kinase-1 modulates pancreatic tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2015 Jan 22;34(4):455-64. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.576. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24561527
-
Poly(I:C) induces controlled release of IL-36γ from keratinocytes in the absence of cell death.Immunol Res. 2015 Dec;63(1-3):228-35. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8692-7. Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26407986 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of maspin in the early pregnant mouse endometrium and its role during embryonic implantation.Comp Med. 2012 Jun;62(3):179-84. Comp Med. 2012. PMID: 22776050 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc6 contributes to abrogating the G1 checkpoint under hypoxic conditions in HPV E7 expressing cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 7;7(1):2927. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03060-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28592805 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of respiratory papillomatosis with malignant transformation by erlotinib in a kidney transplant recipient.BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Aug 28;2013:bcr2013008757. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-008757. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23986124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Monk BJ, Tewari KS. The spectrum and clinical sequelae of human papillomavirus infection. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;107:S6–S13. - PubMed
-
- Vambutas A, Di Lorenzo TP, Steinberg BM. Laryngeal papilloma cells have high levels of epidermal growth factor receptor and respond to epidermal growth factor by a decrease in epithelial differentiation. Cancer Res. 1993;53:910–914. - PubMed
-
- Johnston D, Hall H, Dilorenzo TP, Steinberg BM. Elevation of the epidermal growth factor receptor and dependent signaling in human papillomavirus-infected laryngeal papillomas. Cancer Res. 1999;59:968–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

