Interstitial cells of Cajal, macrophages and mast cells in the gut musculature: morphology, distribution, spatial and possible functional interactions
- PMID: 20132411
- PMCID: PMC3823114
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01025.x
Interstitial cells of Cajal, macrophages and mast cells in the gut musculature: morphology, distribution, spatial and possible functional interactions
Abstract
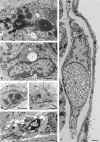
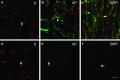
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) are recognized as pacemaker cells for gastrointestinal movement and are suggested to be mediators of neuromuscular transmission. Intestinal motility disturbances are often associated with a reduced number of ICC and/or ultrastructural damage, sometimes associated with immune cells. Macrophages and mast cells in the intestinal muscularis externa of rodents can be found in close spatial contact with ICC. Macrophages are a constant and regularly distributed cell population in the serosa and at the level of Auerbach's plexus (AP). In human colon, ICC are in close contact with macrophages at the level of AP, suggesting functional interaction. It has therefore been proposed that ICC and macrophages interact. Macrophages and mast cells are considered to play important roles in the innate immune defence by producing pro-inflammatory mediators during classical activation, which may in itself result in damage to the tissue. They also take part in alternative activation which is associated with anti-inflammatory mediators, tissue remodelling and homeostasis, cancer, helminth infections and immunophenotype switch. ICC become damaged under various circumstances - surgical resection, possibly post-operative ileus in rodents - where innate activation takes place, and in helminth infections - where alternative activation takes place. During alternative activation the muscularis macrophage can switch phenotype resulting in up-regulation of F4/80 and the mannose receptor. In more chronic conditions such as Crohn's disease and achalasia, ICC and mast cells develop close spatial contacts and piecemeal degranulation is possibly triggered.
Figures
References
-
- Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Klüppel M, et al. W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature. 1995;373:347–9. - PubMed
-
- Thuneberg L. Interstitial cells of Cajal: intestinal pacemaker cells? Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1982;71:1–130. - PubMed
-
- Mikkelsen HB, Thuneberg L, Rumessen JJ, et al. Macrophage-like cells in the muscularis externa of mouse small intestine. Anat Rec. 1985;213:77–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

