Evidence that pregabalin reduces neuropathic pain by inhibiting the spinal release of glutamate
- PMID: 20132471
- PMCID: PMC4492734
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06625.x
Evidence that pregabalin reduces neuropathic pain by inhibiting the spinal release of glutamate
Abstract
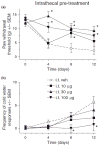
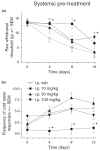
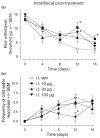
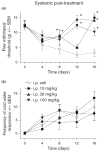
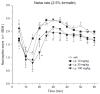
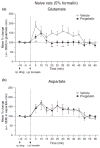
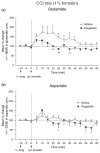
Pregabalin is an anti-convulsant that successfully treats many neuropathic pain syndromes, although the mechanism of its anti-hyperalgesic action remains elusive. This study aims to help delineate pregabalin's anti-hyperalgesic mechanisms. We assessed the effectiveness of pregabalin at decreasing mechanical and cold hypersensitivity induced in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Thus, we compared the effectiveness of pre- or post-treatment with systemic or intrathecal (i.t.) pregabalin at reducing the development and maintenance of the neuropathic pain symptoms. Pregabalin successfully decreased mechanical and cold hypersensitivity, as a pre-treatment, but was less effective at suppressing cold hypersensitivity when administered as a post-treatment. Furthermore, both i.t. and systemic administration of pregabalin were effective in reducing the behavioral hypersensitivity, with the exception of systemic post-treatment on cold hypersensitivity. We also examined pregabalin's effects at inhibiting hind paw formalin-induced nociception in naïve rats and formalin-induced release of excitatory amino acids in the spinal cord dorsal horn (SCDH) both in naïve rats and in rats with neuropathic pain. Pregabalin dose-dependently reduced nociceptive scores in the formalin test. We also present the first evidence that pregabalin reduces the formalin-induced release of glutamate in SCDH. Furthermore, i.t. pregabalin reduces the enhanced noxious stimulus-induced spinal release of glutamate seen in neuropathic rats. These data suggest that pregabalin reduces neuropathic pain symptoms by inhibiting the release of glutamate in the SCDH.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by a contract from Pfizer Corporation the manufacturer of pregabalin and TJC has received consulting funds from Pfizer Corporation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence that gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by inhibiting the spinal release of glutamate.J Neurochem. 2005 Aug;94(4):1131-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03263.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 16092950
-
A comparison of the glutamate release inhibition and anti-allodynic effects of gabapentin, lamotrigine, and riluzole in a model of neuropathic pain.J Neurochem. 2007 Mar;100(5):1289-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04304.x. Epub 2007 Jan 11. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17241130
-
Systemic pregabalin attenuates facial hypersensitivity and noxious stimulus-evoked release of glutamate in medullary dorsal horn in a rodent model of trigeminal neuropathic pain.Neurochem Int. 2013 May;62(6):831-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.02.022. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Neurochem Int. 2013. PMID: 23454190 Free PMC article.
-
Pregabalin suppresses spinal neuronal hyperexcitability and visceral hypersensitivity in the absence of peripheral pathophysiology.Anesthesiology. 2011 Jul;115(1):144-52. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31821f6545. Anesthesiology. 2011. PMID: 21602662 Free PMC article.
-
Pregabalin in the management of central neuropathic pain.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007 Dec;8(17):3035-41. doi: 10.1517/14656566.8.17.3035. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 18001262 Review.
Cited by
-
Spinal cord stimulation modulates supraspinal centers of the descending antinociceptive system in rats with unilateral spinal nerve injury.Mol Pain. 2015 Jun 24;11:36. doi: 10.1186/s12990-015-0039-9. Mol Pain. 2015. PMID: 26104415 Free PMC article.
-
The α2δ-1-NMDA Receptor Complex Is Critically Involved in Neuropathic Pain Development and Gabapentin Therapeutic Actions.Cell Rep. 2018 Feb 27;22(9):2307-2321. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.021. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29490268 Free PMC article.
-
Topical combinations to treat microvascular dysfunction of chronic postischemia pain.Anesth Analg. 2014 Apr;118(4):830-40. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000141. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 24651238 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pregabalin attenuates sensorimotor responses and medullary glutamate release in inflammatory tooth pain model.Neuroscience. 2012 Aug 30;218:359-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.05.016. Epub 2012 May 17. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22609939 Free PMC article.
-
Topical combinations aimed at treating microvascular dysfunction reduce allodynia in rat models of CRPS-I and neuropathic pain.J Pain. 2013 Jan;14(1):66-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2012.10.004. J Pain. 2013. PMID: 23273834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baron R, Brunnmuller U, Brasser M, May M, Binder A. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia: Open-label, non-comparative, flexible-dose study. Eur J Pain. 2008;12:850–858. - PubMed
-
- Bauer CS, Nieto-Rostro M, Rahman W, Tran-Van-Minh A, Ferron L, Douglas L, Kadurin I, Sri Ranjan Y, Fernandez-Alacid L, Millar NS, Dickenson AH, Lujan R, Dolphin AC. The increased trafficking of the calcium channel subunit alpha2delta-1 to presynaptic terminals in neuropathic pain is inhibited by the alpha2delta ligand pregabalin. J Neurosci. 2009;29:4076–4088. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bayer K, Ahmadi S, Zeilhofer HU. Gabapentin may inhibit synaptic transmission in the mouse spinal cord dorsal horn through a preferential block of P/Q-type Ca2+ channels. Neuropharmacology. 2004;46:743–749. - PubMed
-
- Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988;33:87–107. - PubMed
-
- Bian F, Li Z, Offord J, Davis MD, McCormick J, Taylor CP, Walker LC. Calcium channel alpha2-delta type 1 subunit is the major binding protein for pregabalin in neocortex, hippocampus, amygdala, and spinal cord: an ex vivo autoradiographic study in alpha2-delta type 1 genetically modified mice. Brain Res. 2006;1075:68–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

