Increased brain edema in aqp4-null mice in an experimental model of subarachnoid hemorrhage
- PMID: 20132873
- PMCID: PMC2852644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.01.053
Increased brain edema in aqp4-null mice in an experimental model of subarachnoid hemorrhage
Abstract
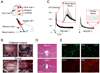
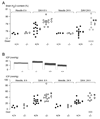
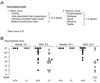
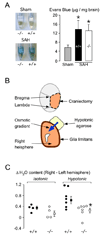
We investigated the role of the glial water channel protein aquaporin-4 in brain edema in a mouse model of subarachnoid hemorrhage in which 30 microl of blood was injected into the basal cisterns. Brain water content, intracranial pressure and neurological score were compared in wildtype and aquaporin-4 null mice. We also measured blood-brain barrier permeability, and the osmotic permeability of the glia limitans, one of the routes of edema elimination. Wildtype and aquaporin-4 null mice had comparable baseline brain water content, intracranial pressure and neurological score. At 6 h after blood injection, aquaporin-4 null mice developed more brain swelling than wildtype mice. Brain water content increased by 1.5+/-0.1% vs. 0.5+/-0.2% (Mean+/-Standard Error, P<0.0005) and intracranial pressure by 36+/-5 vs. 21+/-3 mm Hg (P<0.05) above pre-injection baseline, and neurological score was worse at 18.0 vs. 24.5 (median, P<0.05), respectively. Although subarachnoid hemorrhage produced comparable increases in blood-brain barrier permeability in wildtype and aquaporin-4 null mice, aquaporin-4 null mice had a twofold reduction in glia limitans osmotic permeability. We conclude that aquaporin-4 null mice manifest increased brain edema following subarachnoid hemorrhage as a consequence of reduced elimination of excess brain water.
Copyright 2010 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates brain edema in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: Possible involvement of MMP-9 induced blood-brain barrier disruption and AQP4 expression.Neurosci Lett. 2016 May 16;621:88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.018. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 27080433
-
Potential contribution of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, aquaporin-4, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 to blood-brain barrier disruption and brain edema after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage.J Mol Neurosci. 2012 Sep;48(1):273-80. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9769-6. Epub 2012 Apr 22. J Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22528459
-
Aquaporin-4 facilitates reabsorption of excess fluid in vasogenic brain edema.FASEB J. 2004 Aug;18(11):1291-3. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-1723fje. Epub 2004 Jun 18. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15208268
-
Aquaporin-4 and brain edema.Pediatr Nephrol. 2007 Jun;22(6):778-84. doi: 10.1007/s00467-006-0411-0. Epub 2007 Mar 9. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17347837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies of mdx mice.Neuroscience. 2004;129(4):993-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.08.055. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15561414 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in AQP Research and New Developments in Therapeutic Approaches to Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 18;17(7):1146. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071146. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27438832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-211-5p targeting MMP9 regulates the expressions of AQP4 in traumatic brain injury.Acta Neurol Belg. 2023 Aug;123(4):1321-1329. doi: 10.1007/s13760-023-02205-1. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Acta Neurol Belg. 2023. PMID: 37020131
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C Treatment Enhances Cerebrospinal Fluid Outflow during Toxoplasma gondii Brain Infection but Does Not Improve Cerebral Edema.Am J Pathol. 2024 Feb;194(2):225-237. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.11.008. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Am J Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38065361 Free PMC article.
-
Ifenprodil Improves Long-Term Neurologic Deficits Through Antagonizing Glutamate-Induced Excitotoxicity After Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Transl Stroke Res. 2021 Dec;12(6):1067-1080. doi: 10.1007/s12975-021-00906-4. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Transl Stroke Res. 2021. PMID: 33713028
-
Functionalized Phenylbenzamides Inhibit Aquaporin-4 Reducing Cerebral Edema and Improving Outcome in Two Models of CNS Injury.Neuroscience. 2019 Apr 15;404:484-498. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.01.034. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30738082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badaut J, Brunet JF, Grollimund L, Hamou MF, Magistretti PJ, Villemure JG, Regli L. Aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 expression in human brain after subarachnoid hemorrhage and in peritumoral tissue. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2003;86:495–498. - PubMed
-
- Barry KJ, Gogjian MA, Stein BM. Small animal model for investigation of subarachnoid hemorrhage and cerebral vasospasm. Stroke. 1979;10:538–541. - PubMed
-
- Bloch O, Auguste KI, Manley GT, Verkman AS. Accelerated progression of kaolin-induced hydrocephalus in aquaporin-4-deficient mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:1527–1537. - PubMed
-
- Bloch O, Papadopoulos MC, Manley GT, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 gene deletion in mice increases focal edema associated with staphylococcal brain abscess. J Neurochem. 2005;95:254–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

