Using molecular classification to predict gains in maximal aerobic capacity following endurance exercise training in humans
- PMID: 20133430
- PMCID: PMC2886694
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01295.2009
Using molecular classification to predict gains in maximal aerobic capacity following endurance exercise training in humans
Abstract
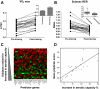
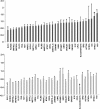
A low maximal oxygen consumption (VO2max) is a strong risk factor for premature mortality. Supervised endurance exercise training increases VO2max with a very wide range of effectiveness in humans. Discovering the DNA variants that contribute to this heterogeneity typically requires substantial sample sizes. In the present study, we first use RNA expression profiling to produce a molecular classifier that predicts VO2max training response. We then hypothesized that the classifier genes would harbor DNA variants that contributed to the heterogeneous VO2max response. Two independent preintervention RNA expression data sets were generated (n=41 gene chips) from subjects that underwent supervised endurance training: one identified and the second blindly validated an RNA expression signature that predicted change in VO2max ("predictor" genes). The HERITAGE Family Study (n=473) was used for genotyping. We discovered a 29-RNA signature that predicted VO2max training response on a continuous scale; these genes contained approximately 6 new single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with gains in VO2max in the HERITAGE Family Study. Three of four novel candidate genes from the HERITAGE Family Study were confirmed as RNA predictor genes (i.e., "reciprocal" RNA validation of a quantitative trait locus genotype), enhancing the performance of the 29-RNA-based predictor. Notably, RNA abundance for the predictor genes was unchanged by exercise training, supporting the idea that expression was preset by genetic variation. Regression analysis yielded a model where 11 single-nucleotide polymorphisms explained 23% of the variance in gains in VO2max, corresponding to approximately 50% of the estimated genetic variance for VO2max. In conclusion, combining RNA profiling with single-gene DNA marker association analysis yields a strongly validated molecular predictor with meaningful explanatory power. VO2max responses to endurance training can be predicted by measuring a approximately 30-gene RNA expression signature in muscle prior to training. The general approach taken could accelerate the discovery of genetic biomarkers, sufficiently discrete for diagnostic purposes, for a range of physiological and pharmacological phenotypes in humans.
Figures


Comment in
-
Does your (genetic) alphabet soup spell "runner"?J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010 Jun;108(6):1452-3. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00268.2010. Epub 2010 Mar 18. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010. PMID: 20299619 No abstract available.
References
-
- Akimoto T, Ribar TJ, Williams RS, Yan Z. Skeletal muscle adaptation in response to voluntary running in Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287: C1311–C1319, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Baar K, Wende AR, Jones TE, Marison M, Nolte LA, Chen M, Kelly DP, Holloszy JO. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to exercise: rapid increase in the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. FASEB J 16: 1879–1886, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Baldwin JE, Krebs H. The evolution of metabolic cycles. Nature 291: 381–382, 1981 - PubMed
-
- Blair SN, Kampert JB, Kohl HW, 3rd, Barlow CE, Macera CA, Paffenbarger RS, Jr, Gibbons LW. Influences of cardiorespiratory fitness and other precursors on cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in men and women. JAMA 276: 205–210, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

