PPAR-gamma coactivator-1alpha regulates progesterone production in ovarian granulosa cells with SF-1 and LRH-1
- PMID: 20133449
- PMCID: PMC5419099
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0352
PPAR-gamma coactivator-1alpha regulates progesterone production in ovarian granulosa cells with SF-1 and LRH-1
Abstract
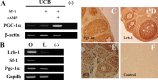
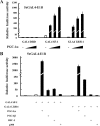
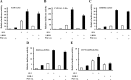
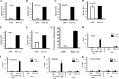
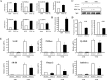
Previously, we demonstrated that bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) differentiate into steroidogenic cells such as Leydig and adrenocortical cells by the introduction of steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1) and treatment with cAMP. In this study, we employed the same approach to differentiate umbilical cord blood (UCB)-derived MSCs. Despite UCB-MSCs differentiating into steroidogenic cells, they exhibited characteristics of granulosa-luteal-like cells. We found that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) was expressed and further induced by cAMP stimulation in UCB-MSCs. Consistent with these results, tissue-specific expression of Pgc-1alpha was observed in rat ovarian granulosa cells. PGC-1alpha binds to the NR5A family [SF-1 and liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1)] of proteins and markedly enhances their transcriptional activities. Reporter assays revealed that PGC-1alpha activated the promoter activities of SF-1 and LRH-1 target genes. Infection of KGN cells (a human cell line derived from granulosa cells) with adenoviruses expressing PGC-1alpha resulted in the induction of steroidogenesis-related genes and stimulation of progesterone production. PGC-1alpha also induced SF-1 and LRH-1, with the latter induced to a greater extent. Knockdown of Pgc-1alpha in cultured rat granulosa cells resulted in attenuation of gene expression as well as progesterone production. Transactivation of the NR5A family by PGC-1alpha was repressed by Dax-1. PGC-1alpha binds to the activation function 2 domain of NR5A proteins via its consensus LXXLL motif. These results indicate that PGC-1alpha is involved in progesterone production in ovarian granulosa cells by potentiating transcriptional activities of the NR5A family proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Stocco C, Telleria C, Gibori G2007. The molecular control of corpus luteum formation, function, and regression. Endocr Rev 28:117–149 - PubMed
-
- Murphy BD2000. Models of luteinization. Biol Reprod 63:2–11 - PubMed
-
- Peng N, Kim JW, Rainey WE, Carr BR, Attia GR2003. The role of the orphan nuclear receptor, liver receptor homologue-1, in the regulation of human corpus luteum 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:6020–6028 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

