Disruption of LGI1-linked synaptic complex causes abnormal synaptic transmission and epilepsy
- PMID: 20133599
- PMCID: PMC2840530
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0914537107
Disruption of LGI1-linked synaptic complex causes abnormal synaptic transmission and epilepsy
Abstract
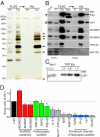
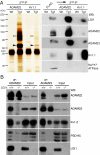
Epilepsy is a devastating and poorly understood disease. Mutations in a secreted neuronal protein, leucine-rich glioma inactivated 1 (LGI1), were reported in patients with an inherited form of human epilepsy, autosomal dominant partial epilepsy with auditory features (ADPEAF). Here, we report an essential role of LGI1 as an antiepileptogenic ligand. We find that loss of LGI1 in mice (LGI1(-/-)) causes lethal epilepsy, which is specifically rescued by the neuronal expression of LGI1 transgene, but not LGI3. Moreover, heterozygous mice for the LGI1 mutation (LGI1(+/-)) show lowered seizure thresholds. Extracellularly secreted LGI1 links two epilepsy-related receptors, ADAM22 and ADAM23, in the brain and organizes a transsynaptic protein complex that includes presynaptic potassium channels and postsynaptic AMPA receptor scaffolds. A lack of LGI1 disrupts this synaptic protein connection and selectively reduces AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Thus, LGI1 may serve as a major determinant of brain excitation, and the LGI1 gene-targeted mouse provides a good model for human epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Noebels JL. The biology of epilepsy genes. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:599–625. - PubMed
-
- Steinlein OK. Genetic mechanisms that underlie epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:400–408. - PubMed
-
- Gu W, Brodtkorb E, Steinlein OK. LGI1 is mutated in familial temporal lobe epilepsy characterized by aphasic seizures. Ann Neurol. 2002;52:364–367. - PubMed
-
- Morante-Redolat JM, et al. Mutations in the LGI1/Epitempin gene on 10q24 cause autosomal dominant lateral temporal epilepsy. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:1119–1128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

