Bacterial translation elongation factor EF-Tu interacts and colocalizes with actin-like MreB protein
- PMID: 20133608
- PMCID: PMC2840354
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911979107
Bacterial translation elongation factor EF-Tu interacts and colocalizes with actin-like MreB protein
Abstract
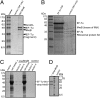
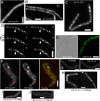
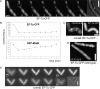
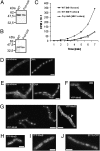
We show that translation initiation factor EF-Tu plays a second important role in cell shape maintenance in the bacterium Bacillus subtilis. EF-Tu localizes in a helical pattern underneath the cell membrane and colocalizes with MreB, an actin-like cytoskeletal element setting up rod cell shape. The localization of MreB and of EF-Tu is interdependent, but in contrast to the dynamic MreB filaments, EF-Tu structures are more static and may serve as tracks for MreB filaments. In agreement with this idea, EF-Tu and MreB interact in vivo and in vitro. Lowering of the EF-Tu levels had a minor effect on translation but a strong effect on cell shape and on the localization of MreB, and blocking of the function of EF-Tu in translation did not interfere with the localization of MreB, showing that, directly or indirectly, EF-Tu affects the cytoskeletal MreB structure and thus serves two important functions in a bacterium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

