Downstream class switching leads to IgE antibody production by B lymphocytes lacking IgM switch regions
- PMID: 20133637
- PMCID: PMC2840363
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0915072107
Downstream class switching leads to IgE antibody production by B lymphocytes lacking IgM switch regions
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 2;110(14):5731
Abstract
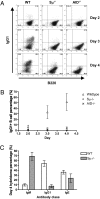
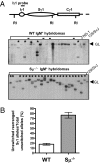
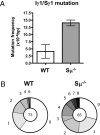
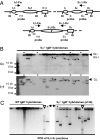
Ig heavy chain (IgH) class-switch recombination (CSR) replaces the IgH C mu constant region exons with one of several sets of downstream IgH constant region exons (e.g., C gamma, C epsilon, or C alpha), which affects switching from IgM to another IgH class (e.g., IgG, IgE, or IgA). Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) initiates CSR by promoting DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) within switch (S) regions flanking the donor C mu (S mu) and a downstream acceptor C(H) (e.g., S gamma, S epsilon, S alpha) that are then joined to complete CSR. DSBs generated in S mu frequently are joined within S mu to form internal switch region deletions (ISD). AID-induced ISD and mutations have been considered rare in downstream S regions, suggesting that AID targeting to these S regions requires its prior recruitment to S mu. We have now assayed for CSR and ISD in B cells lacking S mu (S mu(-/-) B cells). In S mu(-/-) B cells activated for CSR to IgG1 and IgE, CSR to IgG1 was greatly reduced; but, surprisingly, CSR to IgE occurred at nearly normal levels. Moreover, normal B cells had substantial S gamma1 ISD and increased mutations in and near S gamma1, and levels of both were greatly increased in S mu(-/-) B cells. Finally, S mu(-/-) B cells underwent downstream CSR between S gamma1 and S epsilon on alleles that lacked S mu CSR to these sequences. Our findings show that AID targets downstream S regions independently of CSR with Smu and implicate an alternative pathway for IgE class switching that involves generation and joining of DSBs within two different downstream S regions before S mu joining.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dudley DD, Chaudhuri J, Bassing CH, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination versus class switch recombination: Similarities and differences. Adv Immunol. 2005;86:43–112. - PubMed
-
- Honjo T, et al. Rearrangements of immunoglobulin genes during differentiation and evolution. Immunol Rev. 1981;59:33–67. - PubMed
-
- Honjo T. Immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:499–528. - PubMed
-
- Muramatsu M, et al. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell. 2000;102:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Revy P, et al. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) deficiency causes the autosomal recessive form of the Hyper-IgM syndrome (HIGM2) Cell. 2000;102:565–575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

