Histone modification levels are predictive for gene expression
- PMID: 20133639
- PMCID: PMC2814872
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909344107
Histone modification levels are predictive for gene expression
Abstract
Histones are frequently decorated with covalent modifications. These histone modifications are thought to be involved in various chromatin-dependent processes including transcription. To elucidate the relationship between histone modifications and transcription, we derived quantitative models to predict the expression level of genes from histone modification levels. We found that histone modification levels and gene expression are very well correlated. Moreover, we show that only a small number of histone modifications are necessary to accurately predict gene expression. We show that different sets of histone modifications are necessary to predict gene expression driven by high CpG content promoters (HCPs) or low CpG content promoters (LCPs). Quantitative models involving H3K4me3 and H3K79me1 are the most predictive of the expression levels in LCPs, whereas HCPs require H3K27ac and H4K20me1. Finally, we show that the connections between histone modifications and gene expression seem to be general, as we were able to predict gene expression levels of one cell type using a model trained on another one.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

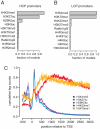
 corresponds to a vector of length L (the number of promoters), where the components are the transformed levels of a histone modification i (
corresponds to a vector of length L (the number of promoters), where the components are the transformed levels of a histone modification i ( , with Ni representing the number of tags in each promoter), a is the y intercept , and the bi to the slope associated with
, with Ni representing the number of tags in each promoter), a is the y intercept , and the bi to the slope associated with  . y denotes a vector of length L whose components are the expression values. In the one-modification models, i can be any of the 39 modifications or two control IgG antibodies. In the two-modifications models, i and j are chosen to cover all combinations of two modifications without repetition. In the three-modifications models, i, j, and k are chosen to cover all combinations of three modifications without repetition. The full model incorporates all 41 variables.
. y denotes a vector of length L whose components are the expression values. In the one-modification models, i can be any of the 39 modifications or two control IgG antibodies. In the two-modifications models, i and j are chosen to cover all combinations of two modifications without repetition. In the three-modifications models, i, j, and k are chosen to cover all combinations of three modifications without repetition. The full model incorporates all 41 variables.
References
-
- Davey CA, Sargent DF, Luger K, Maeder AW, Richmond TJ. Solvent mediated interactions in the structure of the nucleosome core particle at 1.9 a resolution. J Mol Biol. 2002;319(5):1097–1113. - PubMed
-
- Kornberg RD. Chromatin structure: A repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974;184(4139):868–871. - PubMed
-
- Kornberg RD, Thomas JO. Chromatin structure; oligomers of the histones. Science. 1974;184(4139):865–868. - PubMed
-
- Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1997;389(6648):251–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

