No difference in kinetics of tau or histone phosphorylation by CDK5/p25 versus CDK5/p35 in vitro
- PMID: 20133653
- PMCID: PMC2840295
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912718107
No difference in kinetics of tau or histone phosphorylation by CDK5/p25 versus CDK5/p35 in vitro
Abstract
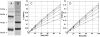
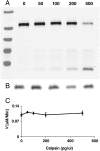
CDK5/p35 is a cyclin-dependent kinase essential for normal neuron function. Proteolysis of the p35 subunit in vivo results in CDK5/p25 that causes neurotoxicity associated with a number of neurodegenerative diseases. Whereas the mechanism by which conversion of p35 to p25 leads to toxicity is unknown, there is common belief that CDK5/p25 is catalytically hyperactive compared to CDK5/p35. Here, we have compared the steady-state kinetic parameters of CDK5/p35 and CDK5/p25 towards both histone H1, the best known substrate for both enzymes, and the microtubule-associated protein, tau, a physiological substrate whose in vivo phosphorylation is relevant to Alzheimer's disease. We show that the kinetics of both enzymes are the same towards either substrate in vitro. Furthermore, both enzymes display virtually identical kinetics towards individual phosphorylation sites in tau monitored by NMR. We conclude that conversion of p35 to p25 does not alter the catalytic efficiency of the CDK5 catalytic subunit by using histone H1 or tau as substrates, and that neurotoxicity associated with CDK5/p25 is unlikely attributable to CDK5 hyperactivation, as measured in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
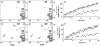

References
-
- Ishiguro K, et al. A serine/threonine proline kinase activity is included in the tau protein kinase fraction forming a paired helical filament epitope. Neurosci Lett. 1991;128:195–8. - PubMed
-
- Ishiguro K, et al. Tau protein kinase I converts normal tau protein into A68-like component of paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:10897–901. - PubMed
-
- Lew J, Beaudette K, Litwin CM, Wang JH. Purification and characterization of a novel proline-directed protein kinase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13383–90. - PubMed
-
- Lew J, Winkfein RJ, Paudel HK, Wang JH. Brain proline-directed protein kinase is a neurofilament kinase which displays high sequence homology to p34cdc2. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:25922–6. - PubMed
-
- Lew J, Wang JH. Neuronal cdc2-like kinase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:33–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

