Prolonged sensory-selective nerve blockade
- PMID: 20133669
- PMCID: PMC2840479
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911542107
Prolonged sensory-selective nerve blockade
Abstract
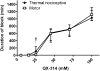
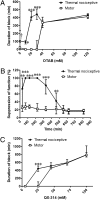
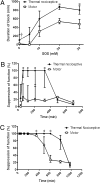
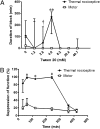
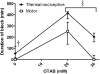
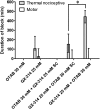
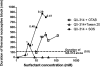
Sensory-selective local anesthesia has long been a key goal in local anesthetic development. For example, it allows women to be pain-free during labor without compromising their ability to push. Here we show that prolonged sensory-selective nerve block can be produced by specific concentrations of surfactants-such as are used to enhance drug flux across skin-in combination with QX-314, a lidocaine derivative that has relative difficulty penetrating nerves. For example, injection of 25 mM QX-314 in 30 mM octyltrimethylammonium bromide (OTAB) lasted up to 7 h. Sensory selectivity was imparted to varying degrees by cationic, neutral, and anionic surfactants, and also was achieved with another lidocaine derivative, QX-222. Simultaneous injection of OTAB at a s.c. injection site remote from the sciatic nerve did not result in prolonged sensory-specific nerve blockade from QX-314, suggesting that the observed effect is due to a local interaction between the surfactant and the lidocaine derivative, not a systemic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Binshtok AM, Bean BP, Woolf CJ. Inhibition of nociceptors by TRPV1-mediated entry of impermeant sodium channel blockers. Nature. 2007;449:607–610. - PubMed
-
- Courtney KR. Mechanism of frequency-dependent inhibition of sodium currents in frog myelinated nerve by the lidocaine derivative GEA. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975;195:225–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

