Dynamic regulation of functionally distinct virus-specific T cells
- PMID: 20133680
- PMCID: PMC2840453
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0915168107
Dynamic regulation of functionally distinct virus-specific T cells
Abstract
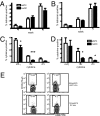
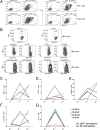
The functional capacities of CD8(+) T cells important for virus clearance are influenced by interactions with antigen presenting cells (APCs) and CD4(+) T cells during initial selection, subsequent expansion, and development of memory. Recently, investigators have shown that polyfunctional T cells correlate best with long-term protection, however, it is still unknown how to stimulate T cells to achieve these responses. To study this, we examined the phenotypes and functions of CD8(+) T cells specific for two different virus antigens stimulated ex vivo using either autologous monocyte-derived dendritic cells (moDCs) or HLA-A2-Ig-based artificial APCs (aAPCs). Although similar numbers of influenza virus and measles virus tetramer-positive cells were generated by stimulation with peptide-loaded moDCs and aAPCs, T cell function, assessed by expression of IL-2, IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, MIP1beta, and CD107a, showed that aAPC-generated CD8(+) T cells were multifunctional, whereas moDC-generated cells were mostly monofunctional. aAPC-generated cells also produced more of each cytokine per cell than CD8(+) T cells generated with moDCs. These phenotypes were not fixed, as changing the culture conditions of expanding T cells from aAPCs to moDCs, and moDCs to aAPCs, reversed the phenotypes. We conclude that CD8(+) T cells are heterogeneous in their functionality and that this is dependent, in a dynamic way, on the stimulating APC. These studies will lead to understanding the factors that influence induction of optimal CD8(+) T cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Topham DJ, Tripp RA, Doherty PC. CD8+ T cells clear influenza virus by perforin or Fas-dependent processes. J Immunol. 1997;159:5197–5200. - PubMed
-
- Moskophidis D, Cobbold SP, Waldmann H, Lehmann-Grube F. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection: Treatment of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-infected mice with monoclonal antibodies reveals that Lyt-2+ T lymphocytes mediate clearance of virus and regulate the antiviral antibody response. J Virol. 1987;61:1867–1874. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

