LIM protein Ajuba functions as a nuclear receptor corepressor and negatively regulates retinoic acid signaling
- PMID: 20133701
- PMCID: PMC2840334
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0908656107
LIM protein Ajuba functions as a nuclear receptor corepressor and negatively regulates retinoic acid signaling
Abstract
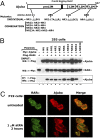
Corepressors play an essential role in nuclear receptor-mediated transcriptional repression. In general, corepressors directly bind to nuclear receptors via CoRNR boxes (L/I-X-X-I/V-I) in the absence of ligand and appear to act as scaffolds to further recruit chromatin remodeling complexes to specific target genes. Here, we describe the identification of the multiple LIM domain protein Ajuba as a unique corepressor for a subset of nuclear hormone receptors. Ajuba contains functional nuclear-receptor interacting motifs and selectively interacts with retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and rexinoid receptor (RXRs) subtypes in a ligand-dependent manner. Simultaneous mutation of these motifs abolishes RAR binding and concomitantly leads to loss of repression on RARE reporter genes. P19 cells depleted of Ajuba are highly sensitized to all-trans retinoic acid (atRA)-induced transcription and differentiation. In the absence of atRA, Ajuba can be readily found at the RARE control elements of RAR endogenous target genes. Stimulation of cells with atRA results in the dissociation of Ajuba from these regions. Moreover, we observed that coexpression of the known Ajuba binding partner Prmt5 (protein arginine methyltransferase-5) inhibited the Ajuba/RAR interaction. The high-affinity Ajuba-RAR/RXR interaction site overlaps the region responsible for Ajuba/Prmt5 binding, and thus binding appears to be mutually exclusive, providing a potential mechanism for these observations. Identification of Ajuba as a unique corepressor for nuclear receptors sheds new light on mechanisms for nuclear receptor-mediated repression and provides a unique target for developing more effective therapeutics to modulate this important pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The LIM protein AJUBA recruits protein arginine methyltransferase 5 to mediate SNAIL-dependent transcriptional repression.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 May;28(10):3198-207. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01435-07. Epub 2008 Mar 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18347060 Free PMC article.
-
The corepressor CTBP2 is a coactivator of retinoic acid receptor/retinoid X receptor in retinoic acid signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;33(16):3343-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01213-12. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23775127 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and retinoic acid receptors differentially control the interactions of retinoid X receptor heterodimers with ligands, coactivators, and corepressors.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;17(4):2166-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.4.2166. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9121466 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid soluble vitamins in gene regulation.Biofactors. 1999;10(2-3):91-7. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520100202. Biofactors. 1999. PMID: 10609868 Review.
-
Dynamic and combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs).Nucl Recept Signal. 2009 May 8;7:e005. doi: 10.1621/nrs.07005. Nucl Recept Signal. 2009. PMID: 19471584 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Essential role of Wtip in mouse development and maintenance of the glomerular filtration barrier.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 Sep 1;323(3):F272-F287. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00051.2022. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35862649 Free PMC article.
-
An emerging link between LIM domain proteins and nuclear receptors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Jun;75(11):1959-1971. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2774-3. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29428964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The LIM protein Ajuba recruits DBC1 and CBP/p300 to acetylate ERα and enhances ERα target gene expression in breast cancer cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Mar 18;47(5):2322-2335. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1306. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30597111 Free PMC article.
-
Shelterin complex and associated factors at human telomeres.Nucleus. 2011 Mar-Apr;2(2):119-35. doi: 10.4161/nucl.2.2.15135. Nucleus. 2011. PMID: 21738835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cytoskeletal Protein Zyxin Inhibits Retinoic Acid Signaling by Destabilizing the Maternal mRNA of the RXRγ Nuclear Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 17;23(10):5627. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105627. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marie H, et al. The LIM protein Ajuba is recruited to cadherin-dependent cell junctions through an association with alpha-catenin. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:1220–1228. - PubMed
-
- Hirota T, et al. Aurora-A and an interacting activator, the LIM protein Ajuba, are required for mitotic commitment in human cells. Cell. 2003;114:585–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

