Selective targeting of radiation-resistant tumor-initiating cells
- PMID: 20133717
- PMCID: PMC2840501
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910179107
Selective targeting of radiation-resistant tumor-initiating cells
Abstract
Tumor-initiating cells (TICs) have been shown both experimentally and clinically to be resistant to radiation and chemotherapy, potentially resulting in residual disease that can lead to recurrence. In this study, we demonstrate that TICs isolated from p53 null mouse mammary tumors repair DNA damage following in vivo ionizing radiation more efficiently than the bulk of the tumor cells. Down-regulation of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) was observed both in fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS)-isolated TICs as compared to non-TICs and in TIC-enriched mammospheres as compared to primary tumor cells depleted of TICs. This effect was accompanied by increased Akt signaling, as well as by the direct activation of the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway specifically within the TIC subpopulation by phosphorylation of beta-catenin on serine 552. Using limiting dilution transplantation performed on p53 null tumor cells transduced with Wnt reporter lentivirus, we demonstrated that FACS sorting of cells expressing TOP-eGFP resulted in a marked enrichment for TICs. Furthermore, FACS analysis demonstrated that cells with active Wnt signaling overlapped with the TIC subpopulation characterized previously using cell surface markers. Finally, pharmacological inhibition of the Akt pathway in both mammospheres and syngeneic mice bearing tumors was shown to inhibit canonical Wnt signaling as well as the repair of DNA damage selectively in TICs, sensitizing them to ionizing radiation treatment. Thus, these results suggest that pretreatment with Akt inhibitors before ionizing radiation treatment may be of potential therapeutic benefit to patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


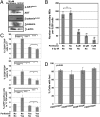
 , Lin−CD29HCD24H; ▪, Lin−CD29HCD24L; □, Lin−CD29LCD24H; ■, Lin−CD29LCD24L. (B) Western blot demonstrates activation of AKT and increased p-β-cateninSer552, a direct target of Akt activation, in freshly FACS isolated TICs, as well as in MSs enriched for TICs, as compared to non-TICs and the total tumor cells cultured on plastic (2D), which are depleted in TICs, respectively.
, Lin−CD29HCD24H; ▪, Lin−CD29HCD24L; □, Lin−CD29LCD24H; ■, Lin−CD29LCD24L. (B) Western blot demonstrates activation of AKT and increased p-β-cateninSer552, a direct target of Akt activation, in freshly FACS isolated TICs, as well as in MSs enriched for TICs, as compared to non-TICs and the total tumor cells cultured on plastic (2D), which are depleted in TICs, respectively.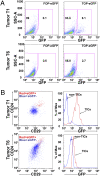
References
-
- Li X, et al. Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:672–679. - PubMed
-
- Watson SA. Oncogenic targets of beta-catenin-mediated transcription in molecular pathogenesis of intestinal polyposis. Lancet. 2001;357:572–573. - PubMed
-
- Reya T, et al. A role for Wnt signalling in self-renewal of haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2003;423:409–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

